Five Key Areas of CX Agent Evolution
By: Execs In The Know
The customer experience (CX) industry was rapidly evolving prior to the pandemic and this evolution shows no signs of slowing down. In fact, the impact of COVID-19 forced many organizations to accelerate strategic initiatives to respond to evolving customer and employee needs. Technology, work-from-home (WFH) staffing models, and customer behavior are just a few factors altering the complexion of contact centers. So, many organizations are now taking an even closer look at what these changes will mean for them as they prepare for the next generation contact center and agent.
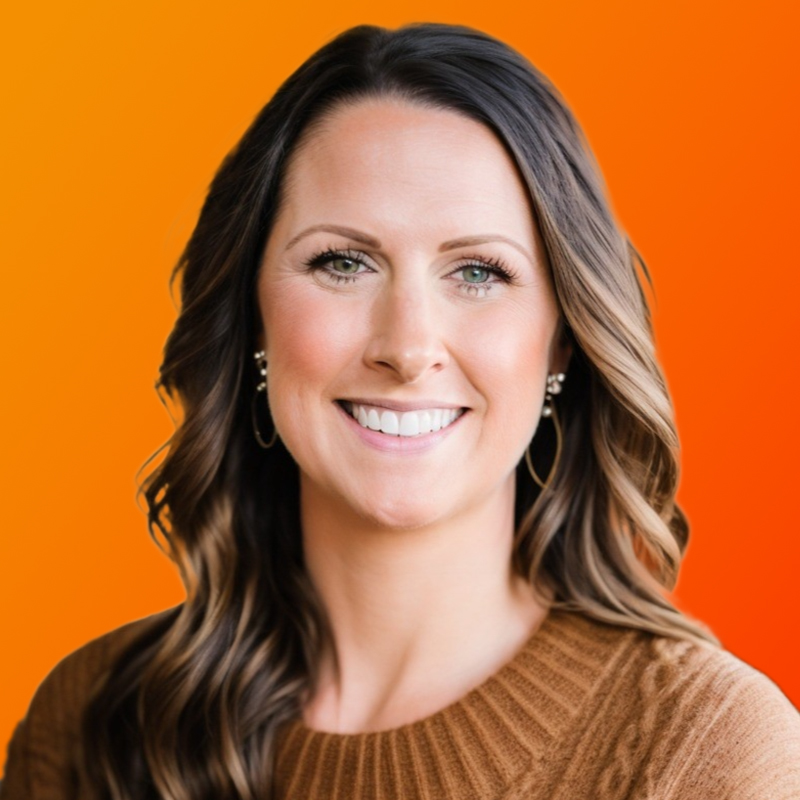
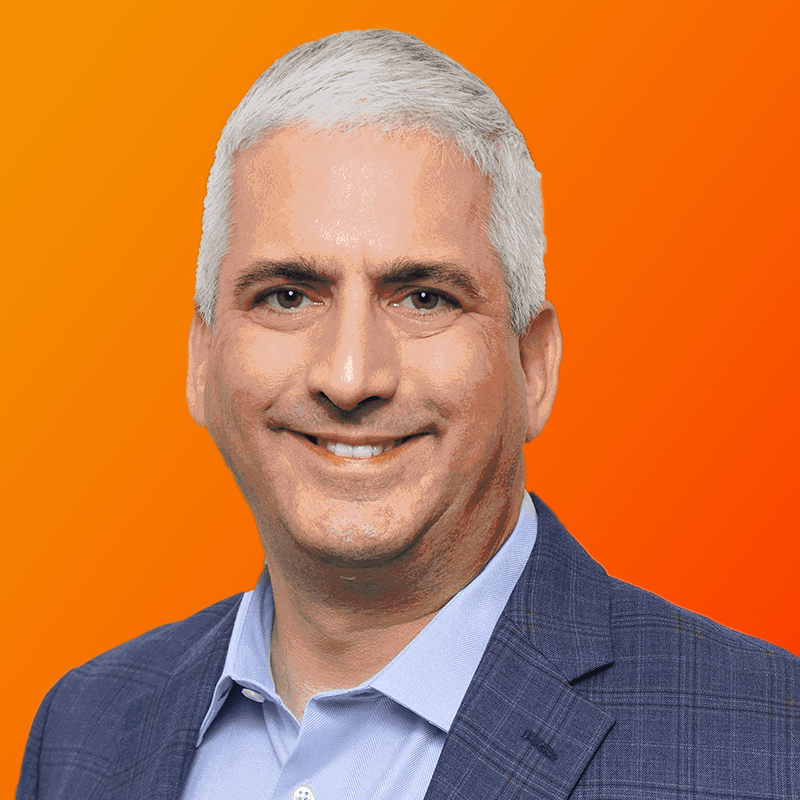
Two industry leaders have provided their valuable perspectives about how they are preparing their own organizations for the future. These leaders are Amber LeGrett, Senior Vice President of Client Experience with Bank of America (BofA) and Anindya Sundar Das, Senior Director and Head of Global Service Design with Uber.
 Amber LeGrett Amber LeGrett
|
 Anindya Sundar Das Anindya Sundar Das
|
Overview
Before discussing the next generation contact center and agent specifically, it is important to understand, from the customer’s perspective, how they will be interacting with organizations as technology continues to evolve.
The rise in digital capabilities and engagement transforms how customers resolve issues.
BofA is a great example of this. The company is known for its mobile app, and in late 2020 launched Life Plan®, a high-tech and high-touch experience that enables clients to set and track near- and long-term financial goals based on their unique life priorities. Additionally, clients can receive personalized guidance and recommendations and the ability to directly schedule in-person or virtual one-on-one appointments with a BofA financial professional.
Digital engagement has also surged, especially with its artificial intelligence (AI)-driven, virtual financial assistant, Erica®. Clients can request help from Erica for a range of everyday banking actions, including searching past transactions, accessing rewards, viewing balances, activating a card, viewing bills and scheduling payments, transferring money, setting up alerts, and more. Erica can tackle more complex tasks by providing personalized, proactive guidance and insights. Ninety-nine percent of clients who engage with Erica can find the information they need without calling a contact center. As LeGrett explained, “We are committed to delivering exceptional experiences to our clients no matter how they prefer to interact and manage
their finances.”
Uber has long been at the forefront of innovation, with customers able to complete many requests via their mobile app. Expanded functionality, capabilities, and personalization are always evolving to meet Uber customers where they are.
Just considering these two forward-thinking companies alone, it is easy to see that more and more activities that once required a human will be handled by technology.
Self-service and digital channel adoption requires higher-skilled agents
 Transactions handled by agents will continue to become more complex. However, while an increasing percentage of simple issues will be resolved by technology, customers still want the ability to speak to an agent, especially with a complex or emotional issue. Results from the 2020 Consumer Edition of the Customer Experience Management Benchmark Series bears this out with 68% of consumers stating that if they knew their issue would be resolved, they would prefer the help of a live agent. Further, when automation cannot address the customer’s issue, human intervention is required. As Sundar Das with stated, this means that in the future, agents with higher IQ and EQ will be required.
Transactions handled by agents will continue to become more complex. However, while an increasing percentage of simple issues will be resolved by technology, customers still want the ability to speak to an agent, especially with a complex or emotional issue. Results from the 2020 Consumer Edition of the Customer Experience Management Benchmark Series bears this out with 68% of consumers stating that if they knew their issue would be resolved, they would prefer the help of a live agent. Further, when automation cannot address the customer’s issue, human intervention is required. As Sundar Das with stated, this means that in the future, agents with higher IQ and EQ will be required.
For example, in Uber’s case, think of a safety issue that is reported to customer service – a machine would not be well-suited to handle that, but an empathetic agent with high emotional intelligence is critical. If handled incorrectly, the consequences are disastrous. So, the skill levels needed in future will be greater than what is normal today.
Similarly, for BofA, consider a client who is experiencing a complicated life change such as a deceased spouse or family member. This requires an agent with a special touch to not simply resolve their issue, but do so with great sensitivity.
In addition to high emotional intelligence, more advanced problem-solving skills are required, as well as technical ability to leverage multiple tools, data sources, and knowledge bases to effectively support the customer.
Five key areas to address evolving agent requirements
With this as the backdrop, it is clear the agent profile and processes will need to change as the nature of transactions and customer expectations change. To ensure companies can attract and retain the right agents with the right skills, there are five key areas of focus, including:
1) Minimum skills and knowledge required
2) Compensation and benefits
3) Training
4) Agent tools, support, and management
5) Growth and development
Each of these areas are reviewed in detail through the rest of the article.
1 Minimum skills and knowledge required
There is no question that the future agent will require different skills than the agent of two years ago, or even today. Organizations must now start the process of identifying specific skills required and continuously review and adjust as needed. Generally, the overarching skills required for the agent of the future are:
- High emotional intelligence
- Advanced problem-solving skills
- Genuine empathy
- Ability to multi-task
- WFH capabilities
- Technologically savvy
- Fast learners
- Respond well to change
This is the first step, but companies must go a step further and specifically define what these mean for their organization and identify how they will verify agents possess those skills.
For example, what does high emotional intelligence mean specifically? And what type of problem-solving skills are needed? They are likely different for every company, as we can see in the case of BofA and Uber.
BofA EVOLVING SKILLS
BofA agents need to sensitively respond to personal and difficult life circumstances, gently walking the client through the steps they need to take. In this case, the agent is more of an advisor than a contact center agent following a resolution process. BofA is also moving toward “super agents”, where agents will need the ability to handle all types of client situations. This will require advanced problem-solving skills to address each type of situation. As LeGrett explains, “This is a huge benefit to clients because they will no longer be transferred to resolve multiple types of issues.” Additionally, with a “digital-first” strategy, BofA agents are tasked with educating clients on how to resolve simpler issues with technology. This, too, requires different skills to help the client resolve their issue in the moment but, also hold their hand through the education process.
UBER EVOLVING SKILLS
In Uber’s situation, agents need the ability to immediately recognize when an extreme customer situation is unfolding and assure the customer they are in good hands. From a problem-solving and technological capabilities perspective, Uber explains, “Agents will need to make sense out of what the ‘machine’ has done, why it did not resolve an issue, and seamlessly pick up where it left off to resolve the issue.” Uber also will need people who: can solve complex problems; have a high degree of curiosity and desire to learn; and are fast learners to respond to the rapid rate of change.
Conclusion: Determine specifically what your agent of the future (short and long term) need. Remove any bias or pre-conceived notions from your mind, without considering your current profile. Be specific on exactly what agents will be required to do. This is the place you start because without this foundation in place, everything else will fall short.
2 Compensation and benefits
Everyone is in the same boat, so higher skilled employees will be in great demand. Compensation is certainly one factor that must be investigated to ensure pay is aligned with required skills and market demand. This has cost implications but the critical interaction with the customer can make or break the customer’s experience and long-term loyalty. As LeGrett said, “Across the board, people want to work where they feel valued, and companies will need to evolve their wages and benefits to stay competitive. After all, a satisfied employee who is valued and supported by their company will, in turn, take care of customers.”

BofA COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS STRATEGIES
In May 2021, BofA’s CEO announced several major investments, including an increase to the minimum hourly wage for U.S. employees to $25 by 2025. Since 2010, the bank’s minimum hourly wage has increased more than 121%. The company also requires their U.S vendors to pay staff $15/hour or more to ensure fair and competitive compensation for any employee providing BofA services. They are also expanding its childcare benefit programs starting July 1, which provides childcare reimbursement up to $275 per month, per child, for U.S. employees with up to $100,000 in cash compensation. And for the 10th year in a row, they will not increase medical healthcare premiums for U.S. employees earning less than $50,000 in 2022 to help address rising healthcare costs.
UBER COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS STRATEGIES
Sundar Das explained, “It is difficult to estimate how these changes will shape salaries and benefits from an absolute dollar perspective, but we’ll of course maintain it at attractive levels. But the structure of compensation will differ greatly from what we have today.” He went
on to say that Uber has always been creative about finding different types of compensation and benefits, and they continue to do that. In his words, “all options are on the table.” There are many factors at play as Uber considers compensation, some favoring pay increases and others that do not. Some of the significant factors impacting these decisions are WFH, consolidation in the industry, need for higher-skilled agents, return to onshoring, and gig work.
Conclusion: The compensation and benefits structure of the past will likely become obsolete given the future landscape. While all companies may not have the luxury of increasing pay significantly, decisions need to be made with the end-goal in mind. There are outside the box solutions, such as flexible work schedules or ability to take personal days versus just sick days. Regardless of approach, packages need to match the market demand and skills required to ensure you attract and retain the right candidates.

3 Training
Attracting and recruiting staff with the right skills is one part of the equation. As transactions become more complicated and more staff are working remotely, training approaches need to be reimagined to be more dynamic, easier to consume, and more practical.
BofA’S TRAINING PERSPECTIVES:
BofA’s training organization, The Academy, offers a variety of hands-on, experiential learning opportunities and innovative training formats. The bank is piloting several emerging technologies that can simulate real-life scenarios that their agents would likely encounter in their day-to-day jobs in a virtual practice environment. These solutions allow employees to immerse themselves in the learning environment and get real-world practice before they start in their roles. LeGrett explained,
“Employees who use simulator technology in their training report feeling more prepared and confident in their positions, which leads to a better overall experience for both employees and our clients.”
UBER’S TRAINING PERSPECTIVES
Sundar Das believes, “In the next few years, call center agents will need to morph from being firefighters to being concierges. Therefore, training curricula and methodology should look different.” For example, more formal coaching programs and real-time feedback will be utilized versus large waves of classroom training that is more common today. Additionally, Sundar Das explains, “Given the speed at which work is becoming increasingly complex and data-driven, re-skilling at quicker intervals will be
a major focus.” And with WFH here to stay, training will become more dynamic and digital, with more “bite-sized knowledge nuggets.”
Additionally, WFH home agents require much more support during training than in-center agents. So, not only does the actual training itself differ for these agents, but the time required and level of support increases. Anindya further explains that they expect to see an increase in the use of sandbox environments to train WFH agents in life-like situations offline.
Conclusion: Reimagine how you train both new and existing agents. The traditional models of a couple of weeks of classroom training followed by a “nesting” period will likely not be effective. Agents will need much more practical experience through role plays, simulation, and hands-on practice. The training will need to be more visual, dynamic, and in smaller “chunks.” Last, one size does not fit all. WFH training must be designed and implemented differently than in-person.
 4 Agent tools, support, and management
4 Agent tools, support, and management
To ensure agents can do what they do best – solve issues and deliver a superior experience- agent tools are critical. But support and management are equally important. Just as agent skills and knowledge are changing, so too are supervisory skills. Supervisors will also need advanced problem-solving skills, a high degree of empathy, and ability to manage and coach highly skilled agents. And with a dispersed workforce, they need the ability to manage remote workers, which is quite different from in-person. Management also needs to understand that agents of the future will be handling more complex and potentially more emotional transactions. This needs to be considered in policy-making. For example, more flexibility in schedules and the ability to take more frequent (but perhaps shorter) breaks may be necessary. Or more emotional support considering the potential of higher-stress transactions.
BOFA AGENT TOOLS AND SUPPORT
BofA agents can see what clients have done prior to the call, and the company continues to enhance these capabilities and integrate new technologies to be even more nimble in following the end-to-end customer journey.
BofA also recently launched a new mobile app for agents, where they can switch their shifts with a colleague or request a day off, giving them a real-time way of managing their lives and schedules.
UBER AGENT TOOLS AND SUPPORT
Sundar Das explained that AI will be used in several ways to support agents such as intelligent routing to agents, real-time assistance, targeted training, and potentially profile-performance matching. Uber also has many new tools ranging from those that help agents: identify the root causes faster; view the customer’s journey to help them solve the issue (including if a solution has been attempted by automation already); and the ability to quickly get assistance solving the problem. From a support perspective, Uber is committed to supporting agents, considering some of the disconcerting transactions they handle. There are measures in place allowing agents to take time between difficult calls and get counseling if needed. The company has even implemented creative ways to reduce stress such as bringing puppies into the physical center.
Conclusion: For companies who have not yet taken steps to elevate agent-facing tools and technology, it is time. Customers will expect agents to know their journey without repeating themselves. And agents need tools and resources to solve customer issues quickly and effectively. Technology will not solve everything, however. Supervisory skills must be redefined, and the right policies and processes must be implemented to support agents in this new environment.

5 Growth and development
To attract and retain highly skilled agents, career growth and development takes on a new level of importance. As required skills and knowledge change, companies must evaluate existing staff to determine if they have the right skills, and if not, determine if they can learn them.
BofA GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT INITIATIVES
The BofA Academy provides career path tools that are accessible to all associates including formal mentoring programs as well. They offer great programs related to diversity with close to 30 different employee networks that associates can join. This gives them the opportunity to meet executives who sponsor these groups and make connections and be exposed to other opportunities in the company.
UBER GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT INITIATIVES:
Sundar Das eloquently said, “More often than not, people underperform because the role is not suited to them. Roger Federer (professional tennis player) would not be a great baseball player. Understand that everyone has the potential to succeed given the right opportunities and the right matching of skills to the job.” Like many companies, Uber has realized that the contact center represents a huge pool of talent, with agents capable of moving into more strategic and senior roles. So, recruiting and development strategies will change to identify these individuals and give them opportunities to grow into other roles. Sundar Das explains, “Career growth is like rock climbing. It can be diagonal, sideways, or up.” It will be important for supervisors and managers to identify and support this growth. Uber actively focuses on this and has several programs in place such as mentoring programs in which agents are encouraged to seek out mentors.
Conclusion: Contact center agents of the future are looking for careers, not just jobs. This is great news for organizations as they recruit, train, and develop these agents. Employee loyalty benefits the company and the customer. So, organizations should implement processes to proactively identify skills of candidates and existing agents, beyond what is required for the agent role. And then, ensure managers are trained to help agents with career development plans, through formal and informal programs.
In summary
The next generation contact center and agent is here, and most organizations have started this transformation. It involves reimagining all areas that impact the agent and the operation including required skills and recruiting, compensation, training, agent tools and support, and career development. The companies that can think outside the box (stepping away from the status quo) will have a competitive advantage, resulting in highly skilled and loyal employees, driving long-term customer loyalty.

Go Back to All Articles. Have a story idea? Submit to [email protected].
Want to get this publication in your inbox? Subscribe here!
Customer Experience Is Becoming Intelligent: What Leaders Need to Know NowArtificial intelligence is rapidly becoming the intelligence layer within modern customer experience operations. The most impactful organizations are amplifying human capability through cooperative intelligence—embedding AI across the full CX lifecycle to improve efficiency, reduce risk, and unlock entirely new levels of service. In this session, Mark Vange, CTO and Founder of Autom8ly, will share how AI is transforming CX through capabilities including autonomous agents, real-time agent assist, intelligent transcription, automated QA and compliance monitoring, and proactive operational alerting. These systems continuously observe, learn, and adapt from customer interactions—helping organizations improve agent performance, detect fraud and operational waste earlier, and ensure consistent service quality at scale. Critically, these capabilities are now operating successfully in highly regulated environments such as healthcare and financial services, where compliance, auditability, data protection, and operational reliability are non-negotiable. Mark will explore how ROI CX is leveraging this intelligence to enhance service delivery in these demanding environments—empowering agents with real-time insight while strengthening compliance, resilience, and operational control. You’ll learn:
Thanks to Our Partners
|
Beyond Automation: Social CX in the Age of AIAs customer service continues its shift toward social and asynchronous channels, AI is fundamentally changing how brands engage, respond, and scale. Traditional voice and chat are no longer the primary focus; instead, AI is quietly streamlining these channels while social media becomes the front line for service, community building, and brand growth. With rising expectations for responsiveness across earned and owned channels, CX leaders are navigating increased social volume alongside limited, high-risk AI options that can easily feel inauthentic to highly digital consumers. In this session, Chris Wallace, SVP Global Growth at IntouchCX, along with Laura Wheeler, Director of Social Media Customer Care at Audible, examine what this shift means once efficiency is no longer the differentiator. The conversation reframes AI beyond productivity, focusing on the evolving value of CX, demographic nuance by brand, and why human connection remains critical, while also including an interactive breakout session where attendees discuss real-world social CX scenarios and how to apply AI without sacrificing authenticity. Key Takeaways
Thanks to Our Partner
|
Stop Guessing: Take Control of the CX Buying ProcessThe CX technology landscape is expanding at a dizzying pace. With the rapid influx of Voice AI, CCaaS, and agentic tools, distinguishing between “market noise” and “strategic necessity” has never been harder. The biggest hurdle for enterprise leaders isn’t just implementing technology, it’s buying it. Join Simplify and Lindsey Ellison, SVP of Business Technology at Globe Life, for an interactive workshop exploring the complexities of procuring technology for their 13,000+ agent organization. Lindsey will share Globe Life’s journey, identifying strategic market shifts and defining the “why” behind their transformation toward modern CCaas and Agentic AI. Participants will:
Thanks to Our Partner:
|
Where CX Strategy Breaks Through: Designing Ideal-State Journeys for Speed, Loyalty & Operational EfficiencyCustomer journeys often break in predictable places, and those breaks cost you time, money, and loyalty. In this Tech Forum session, we’ll pinpoint where friction hides, show how AI eliminates redundant work, and introduce a journey management model that simplifies experiences without sacrificing empathy. Attendees will walk away with a practical framework and action plan to accelerate resolution, reduce operational costs, and deliver more consistent, intelligent customer experiences. Key Takeaways:
Thanks to Our Partner
|
Your Customer Already Told Us: Building Memory into the Agent EcosystemEvery call transfer is a failure point. Every “can you repeat that?” burns time and trust. Most contact centers respond by adding more AI, which makes the problem worse. Without orchestration, you get conflicting responses, lost context, and agents cleaning up messes they didn’t create. Roger Lee shows what happens when you stop stacking AI tools and start coordinating them. Drawing on examples from organizations that cut contacts by 50% while improving quality, he explains how to design clear boundaries for when AI should act, collaborate, or escalate. Over the next few years, conversation will become the primary interface for getting work done. AI prepares and coordinates tasks before humans step in to handle judgment calls and complex decisions. You’ll learn:
Thanks to Our Partner
|
Leading Execution in the Age of AI and Agentic SystemsWhen AI starts acting on behalf of your team, who is accountable? Customer experience is entering a new phase. AI is no longer limited to chatbots, and copilots’ organizations are now experimenting with agentic AI systems that can take action, make decisions, and orchestrate tasks across workflows. While this shift expands what’s possible, it also raises a critical leadership challenge: how do you move toward greater automation and intelligence without compromising accuracy, trust, and the human quality of care? In this Leader’s Choice session, Sarah brings a perspective shaped by her work at Procedureflow to guide a conversation on a key industry shift from AI assistance to AI action and why this makes operational clarity more important than ever. Participants will explore the realities leaders are facing today: • Chatbots handling first contact but lacking process awareness The discussion will focus on how leading organizations are building a foundation where AI, copilots, and agentic systems operate within structured knowledge, governance, and guided workflows. This ensures frontline teams remain confident; customers receive consistent care, and automation enhances rather than undermines trust. Before the session begins, attendees will note their top questions and challenges with AI-driven execution, which will shape the discussion. These real-world inputs will drive a hands-on group exercise where participants identify care gaps, craft opportunity statements, and map the foundations needed for safe, consistent AI-powered execution. Attendees will leave with a leadership perspective on designing CX environments where intelligence, autonomy, and human judgment work together delivering faster, more personalized service without compromise. Thanks to Our Partner
|
See AI Transform Skill Development LIVE — How Your Peers are Slashing Ramp Time & Accelerating UpskillingFrontline performance is the single biggest driver of customer experience. But traditional training doesn’t scale, doesn’t stick, and rarely prepares teams for real-world customer interactions. In this high-impact session, CX Learning and Operations expert Casey Denby reveals how leading enterprise brands—including Chase, Marriott, State Farm, Comcast, JetBlue, Nordstrom, and MLB—are using AI-powered, lifelike simulations to accelerate skill development and deliver measurable CX results, fast. Casey breaks down the science behind how people actually learn, and shows how AI-driven practice environments dramatically improve retention, confidence, and performance—without adding operational complexity. You won’t just hear how it works. You’ll experience it. In this live, interactive session, you’ll:
Thanks to Our Partner:
|
How Urban Outfitters Cracked the Code on AI AgentsLaunching AI at enterprise scale is never simple, especially across beloved global brands with distinct voices, loyal customers, and complex operational structures. But that’s exactly the challenge Joannah Holmes, Director of Customer Service at URBN, set out to solve. In this mainstage case study, Joannah takes attendees behind the scenes of an ambitious AI agent rollout in modern retail CX. Over a two-week sprint, URBN deployed agentic AI across four marquee brands: Anthropologie, Free People, Urban Outfitters, and Terrain. This session will explore the real story behind the launch: the strategy, the cross-functional alignment, the unexpected hurdles, and the breakthrough moments that made it possible. Joannah will share how her team ensured the AI agents not only mirrored each brand’s identity but also unlocked measurable operational gains to improve speed, accuracy, agent workload, and customer satisfaction. Most importantly, she’ll discuss what she’s learned about responsibly scaling agentic AI inside a global retail ecosystem, and what’s coming next for URBN. Attendees will walk away with a rare, inside look at enterprise AI transformation in motion, including what it really takes, what’s required to build trust, and how to set a foundation for sustainable, scalable impact. Thanks to Our Partner:
|
How Tory Burch and Vuori Implemented Phone AI in 2025Tory Burch herself singled out the CX team at their end-of-year companywide all-hands for the brand’s most successful AI work of 2025. Vuori started their implementation weeks before Black Friday, had time to spare, and flipped skeptical leaders just one quarter post-launch. The question is how. Flip is going behind the scenes with the changemakers who made bold bets, learned fast, and won big. We’ll start at the beginning, when there was little more than ideas, and travel with them through time as they became market experts, pivoted from failed pilots, drove stakeholder alignment, forecasted ROI, and ultimately transformed some of the most iconic American brands. In this session, learn the real-life twists and turns, tradeoffs, hard calls, and big ‘aha’ moments — and how can you use their experience to shortcut your own learnings as you eye bigger, bolder, customer-facing AI deployments in your organization. Key Takeaways:
Thanks to Our Partner:
|
Automation Without Alienation: A People-First Workforce Strategy in the Age of AIThis session shares a real-world transformation story of how a large enterprise contact center moved from early skepticism about automation (“it will replace jobs”) to a people-first strategy that improved both operational performance and employee experience. The speakers will explore the strategic inflection point that led Cigna to adopt real-time automation—and the leadership work required to earn buy-in beyond senior leadership. The discussion will highlight key lessons, measurable outcomes, and how today’s momentum in AI connects to the future of workforce orchestration—illustrating how automation and AI can work together to support scalable, resilient workforce strategies beyond the contact center. Key takeaways for attendees
|
CX Masterclass: A Look at the Ritz-Carlton Culture of ExcellenceExceptional customer experiences don’t happen by chance. They are built through culture, clarity, and disciplined execution. In this masterclass, Amanda Joiner, Global Vice President of The Ritz-Carlton Leadership Center, shares how The Ritz-Carlton has sustained legendary service by empowering employees to truly own the customer experience. The session will explore the core frameworks that guide behavior and decision-making across the organization, including the Credo, Motto, Three Steps of Service, Employee Promise, and the 12 Service Values. Together, these elements establish a shared language for service and a consistent standard for how care shows up in moments that matter. Beyond philosophy, this session will showcase the practical systems that make excellence repeatable: how thoughtful selection, onboarding, recognition, and continuous upskilling reinforce a culture of ownership and enable employees to act with confidence and purpose. Attendees will take away clear, actionable perspectives that elevate service culture across any organization, along with opportunities for peer interaction, guided table discussions, and reflection to help leaders connect the concepts to their own teams and environments.
|
Making CX a C-Suite PriorityCX friction is easy to spot on the front lines and far harder to elevate into an executive priority. Too often, CX leaders come armed with anecdotes or dashboards that resonate locally but fail to translate into enterprise-level urgency. This session explores how leading organizations bridge that gap by pairing a clear narrative with hard data tied to business performance, risk, and customer outcomes, and turning CX pain into an executive ready business case. Through real customer examples, Reddy will examine how a small, focused CX pilot delivered measurable wins that earned CEO attention and sponsorship. Attendees will leave with a practical playbook for translating frontline insight into boardroom language and how to build the internal momentum needed to scale CX initiatives across the enterprise. Thanks to Our Partner:
|
Next Level Learning & Development: The Operational Advantage of Learning Done RightEffortless customer experiences begin with effortless learning—learning that happens inside operations, not alongside them. Next-level Learning and Development blends seamlessly into day-to-day execution, transforming operations into an operational learning environment where learning is strategic, immediate, and continuous. Grounded in cognitive science and adult learning research, these approaches require no new tools or budget, yet deliver immediate, measurable improvements in performance and customer ease. This session challenges the outdated, siloed model where Learning and Development is solely responsible for performance. Instead, it positions performance as a shared operational continuum—owned by leaders, reinforced in the moment, and sustained through science-backed practices. In an era where organizations are racing toward AI without understanding how people actually learn, this conversation returns to the foundations of research, demonstrating how trusted, evidence-based strategies can be applied immediately to maximize performance in dynamic environments. Attendees will learn:
|
Frontline Empowerment: The Heart of CX TransformationTransformation is happening all around us — in technology, AI, and business models — but the real story of customer experience isn’t about systems; it’s about people. In this keynote, Kevin McDorman, Vice President of Customer Care at Southwest Airlines, will share how the frontline isn’t just executing service — it is the strategy for creating seamless, friction-free experiences. Through real stories from Southwest, Kevin will show how empowering frontline teams to act with judgment, empathy, and autonomy drives measurable improvements across every metric. Attendees will see how putting people first — not scripts, dashboards, or automation alone — creates solutions in the moments that matter most, transforms policies into guardrails, and positions technology as a partner, not a replacement. This session challenges leaders to rethink CX strategy: how to anticipate customer needs, remove friction, and give teams the authority to deliver results. Attendees will leave inspired to view the frontline not just as execution, but as the engine of enterprise-wide customer experience. About Kevin Kevin McDorman serves as Vice President of Customer CARE at Southwest Airlines, assuming the role on May 12, 2025. He leads a hybrid workforce of more than 3,500 Employees across the continental U.S., overseeing all Customer-initiated service channels—including phone, email, and social platforms—as well as proactive customer communications, travel disruption strategy and execution, and Southwest’s partnership with the U.S. Department of Transportation. Under Kevin’s leadership, Customer CARE supports more than 140 million Customers traveling through 117 airports across 11 countries, managing over 20 million Customer contacts anually. His organization plays a critical role in delivering the legendary hospitality that defines the Southwest brand—whether helping Customers navigate irregular operations, providing real-time digital communications during travel disruptions, or resolving complex issues with empathy and expertise. Kevin is focused on modernizing the end-to-end Customer journey by integrating digital, operational and voice-of-customer insights; strengthening alignment with departments across the Company; and enabling a consistent Customer support model that reflects Southwest’s culture of service and connection. Prior to joining Southwest, Kevin built a distinguished 22-year career at AT&T, where he held senior roles spanning customer service, call center operations, finance, vendor management, and strategic development. He led organizations supporting more than $100 billion in revenue, oversaw international operations in 16 countries across 12 global outsourcing partners, and delivered a call-center transformation that generated $700 million in operating-expense savings while reducing customer contacts by 32% and lowering cost-to-serve per subscriber by 18% year-over- year. He has a history of delivering best-in-class customer service by leveraging groundbreaking innovation in Big Data, Gen AI, Robotics, and Global Sourcing. Known for his collaborative leadership style, strength in building high- performing teams and ability to connect people, process, and technology, Kevin mentors leaders across functions and drives performance through clarity of vision, purposeful innovation, and customer-centric culture.
|
Exporting Culture: How to Extend Your Brand’s Soul Into an Outsourced CX ModelEvery brand has a culture—few know how to export it. As more companies blend internal CX teams with outsourced BPO partners, the central challenge becomes ensuring that customers experience the same authenticity, empathy, and values no matter who answers the call. In this interactive workshop, GTCX CEO Bill Colton and Azure Standard’s CX leader Karen Slusher unpack how a brand’s “internal DNA” can be successfully extended beyond its four walls. Azure Standard, with its uniquely passionate customer following and deeply relationship-driven approach, has cultivated a CX model where agents are empowered to spend real time with customers, prioritize connection over speed, and build long-term trust. Translating that ethos to an external partner might seem impossible—yet Azure and GTCX have built a blueprint for doing exactly that. Attendees will learn:
This session blends strategic insight with practical guidance from two leaders who have done it in the real world—not in theory. Thanks to Our Partner:
|
The Standard Is the StrategyCX excellence isn’t created by software, scripts, or perfectly defined processes. It’s created by leaders, and the standard they’re willing to set for themselves. In this keynote, Travis Brown, former NFL quarterback and current pastor, delivers a direct challenge to CX executives: your team’s performance will never exceed the standard you personally embody. Travis explores the uncomfortable but liberating truth that success can often mask slipping standards, and teams will always follow the tone the leader sets, especially when conditions aren’t ideal, pressure is high, or you’re leading teams you didn’t personally handpick. This session will reshape how you think about standards, how they’re created, reinforced, and multiplied across the enterprise, and why EX will always dictate CX. Through powerful stories and practical leadership insight, Travis helps leaders see that the most scalable strategy for CX excellence is not a system… it’s a standard. And it starts with you. About Travis: Travis Brown is a former NFL quarterback who played for 6 seasons (Seahawks, Bills, Colts). He now channels his passion for leadership, teamwork, and culture into developing others. He oversees campuses at Christ’s Church of the Valley (CCV)—one of the largest churches in the country with 19 campuses and over 55,000 in attendance every weekend—helping shape environments where teams thrive and people grow. He is also the founder of 180 Sports, a nonprofit dedicated to using sports to impact culture by training coaches, supporting athletes, and providing equipment. Through his experiences on and off the field, Travis has gained a deep understanding of what it takes to build strong teams, cultivate winning cultures, and help individuals reach their full potential. Beyond his professional work, Travis has been married to his wife, Corinna, for nearly 25 years, and together they have five children. His greatest passion is investing in people—whether on the field, in the workplace, or at home—helping them maximize their potential and lead with clarity, resilience, and purpose.
|
Delivering Care Without Compromise: The Human-Tech Partnership at VisaFrom her first job behind a supermarket checkout to leading Visa’s Global Client Care organization, Katie Beaudry has always understood that customer experience begins with empathy. What once required face-to-face presence has evolved into a world where data, AI, and predictive design enable care at scale — yet the heart of CX remains human. In this keynote, Katie will share how Visa is reimagining every stage of the service journey, building “self-healing” experiences and agentic AI systems that empower both customers and care teams to deliver seamless, personalized solutions in real time. But transformation isn’t about technology alone; it’s about foresight, culture, and connection. Katie explores how her teams are blending human intuition with intelligent automation to deliver care without compromise. She’ll challenge leaders to rethink what preemptive service looks like in practice, how to equip teams for success in an AI-powered ecosystem, and how to keep the human touch alive at a global scale. Attendees will walk away inspired to raise the bar, not just by solving customer problems, but by anticipating them. About Katie Katie leads Visa’s Client Care organization, which is part of Client Services. Client Care’s purpose is to provide superior customer support for Visa’s products and services across a full range of client types, from cardholders whom Visa interacts with ‘on behalf of’ banks and credit unions (our revenue-generating managed services departments), to helping merchants, acquirers, fintechs, and other financial institutions directly with their service queries and technical issue resolution. Client Care has more than 1,500 highly skilled team members who support 18 languages, and our award-winning team annually handles 18M customer touchpoints across six channels, including phone, email, live chat, self-service portals, chatbot, and social media. Before joining Visa in February 2022, Katie spent 13 years with HSBC Bank, both in London and New York. Her first role with HSBC started in Corporate Communications, supporting large, multi-year transformation programs for the Finance and Risk functions. She then moved to New York to lead Employee Communications for the US business and progressed to lead the Customer and Employee Experience teams. Later, she ran the US contact center and international banking organizations. Before HSBC, she was a Senior Corporate and Legal Affairs Manager at Tesco in the UK, handling national media and other public relations. She is a co-active coach trained through the Coaches Training Institute and has a joint first-class honors degree in English and Media from Sussex University, UK. She lives in Florida with her husband and has three children. In her spare time, she enjoys traveling, cycling, and eating out.
|
Walmart’s People-Led, Tech-Powered Approach to Customer SupportAs customer and associate support reaches a defining moment, CX leaders are being challenged to evolve faster than ever without losing the human connection that defines great service. In this keynote, Meghan Nicholas, Vice President of Customer Engagement Services at Walmart, will explore how large, complex organizations can modernize their service operations through a people-led, tech-powered approach. Drawing from real-world experience at scale, she will examine how today’s leaders are balancing rising expectations, accelerating technology, and the enduring need for empathy and trust across every customer touchpoint. Attendees will gain perspective on designing service models that are both operationally resilient and deeply human, where innovation enhances, rather than replaces, meaningful connection. With the continued growth of automation, AI, and self-service, this session offers a timely, high-level look at how CX leaders can drive efficiency, clarity, and care simultaneously, setting a new standard for performance without compromise. About Meghan: Meghan Nicholas is a leader in digital transformation, customer experience, and operational strategy. As Vice President of Care Experience and Operations at Walmart, she leads customer and associate contact centers, driving innovations that enhance customer satisfaction while optimizing operations at scale. Meghan is passionate about leveraging technology, data, and AI to streamline processes and eliminate friction in customer interactions. Before joining Walmart, Meghan held leadership roles in supply chain, operations, and analytics at Peloton, Dollar General, and The Home Depot. With deep expertise in operational strategy and customer care, she has led large-scale transformations that drive efficiency, innovation, and business growth in complex, high-volume environments. She holds a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration from Auburn University.
|
CX as a Growth Engine: Proving Value in the BoardroomCustomer experience leaders know that delivering exceptional service drives loyalty, retention, and long-term business value. Yet, securing investment for new tools, talent, and innovations often requires more than intuition or anecdotal wins. Many CX leaders still face challenges in articulating a compelling financial case for investment, translating the less tangible benefits of customer care into metrics that resonate with CFOs, CEOs, and boards. Without a strong internal case, initiatives risk being deprioritized in favor of more easily quantified projects. This panel will dive into proven strategies for building persuasive ROI models that tie customer care excellence directly to revenue growth, reduced churn, and operational efficiency. Panelists will share best practices for quantifying knock-on effects like customer lifetime value, brand advocacy, and competitive differentiation, while also offering guidance on how to educate senior leadership on the true business impact of CX. Attendees will leave with practical tools and storytelling techniques to strengthen their internal advocacy and secure the resources needed to elevate customer experience initiatives. Thanks to Our Partner:
|
Beyond Deployment: The Quality Assurance and Measurement Essentials for AI-Powered CXAs AI reaches new levels of deployment within the contact center, the focus is all too often on speed to market rather than sustained quality and performance. Without rigorous monitoring, these solutions can drift from intended outcomes, generate inconsistent or inaccurate responses, and even erode customer trust. The difference between AI-powered solutions that delight versus ones that frustrate often comes down to how well performance is measured, tuned, re-tuned, and governed over time. This panel will explore why monitoring AI quality must be as much a priority as implementing AI itself. CX leaders will share emerging best practices for establishing performance benchmarks, aligning AI outputs with business and customer goals, and setting up governance models that evolve alongside the technology. Attendees will gain practical insights on how to track both quantitative and qualitative results, run an effective QA layer, detect bias or drift, and create feedback loops that ensure AI remains a reliable extension of the customer experience strategy. During this panel you’ll learn about:
|
CX Livewire: Polling, Predictions, and Instant FeedbackJust as data drives the vital operational adjustments that CX leaders make every day, data also fuels the strategic decisions that power entire programs. During this session, panelists will dive into the data of critical CX topics the goal of contrasting results from recent Execs In The Know’s CX research with live polling of the CRS Amelia Island audience. Real-time insights will help audience members benchmark themselves against the room, while panelists provide headlights into some of the biggest challenges and successes at their own organizations. Come prepared to participate during this high energy, fast-paced session which is sure to produce both surprises and confirmation. Thanks to Our Partner:
|
Beyond Recovery: Shaping a CX Model That Anticipates, Prevents, and DelightsMost service organizations remain focused on reacting to issues after they arise, yet the real opportunity lies in anticipating and preventing problems before customers ever need to reach out. This panel will explore how CX leaders are rethinking their approaches to become more predictive and proactive, leveraging a mix of customer data, journey signals, and emerging AI capabilities to spot friction points early and deliver pre-emptive support. Panelists will discuss both the opportunities and the challenges in shifting from recovery to prevention — from making the internal case for investment in predictive solutions, to building the right organizational support, to ensuring governance and trust remain at the center. Expect practical insights into how companies are both executing and thinking about proactive outreach and empowering agents with “next-best actions,” all while learning from both successes and setbacks. Attendees will leave with a clearer view of how proactive strategies can reduce preventable contacts, elevate satisfaction, and lower costs while strengthening long-term customer relationships. Thanks to Our Partner
|
Uncompromised Leadership — When Self-Respect Becomes PricelessWhen the stakes are high and the pressure is on, real leadership is revealed not by strategy decks or polished statements, but by the courage to act with integrity, even when it costs something. In this intimate discussion, two EITK advisory board members and seasoned senior CX executives share candid stories of when their values were tested under fire. When the easiest choice isn’t the right one, and when standing firm carries personal or professional consequences, this is when true leaders stand firm. We’ll explore how leaders evolve from good intentions to becoming “the one” others can count on: the person who speaks up, takes risks, and acts on their convictions when everyone else stays quiet. The conversation will examine how self-respect becomes the source of leadership courage, fueling trust inside organizations and loyalty among customers. In this session, you’ll learn:
Expect real stories of integrity under pressure—from culture flashpoints to customer-impacting crises—and leave with practical insights on how courage, vulnerability, and personal accountability can transform organizations. Attendees will walk away inspired to embrace self-respect as a leadership operating system that not only protects employees and customers but also creates the foundation for authentic, lasting trust. |
Thanks to Our Partner:
![]()
| Introduction by: |
 Ruth Rose
Vice President of Strategic Growth  |
 Lisa Oswald
Senior Vice President, Customer Service  |
 Carolyne M. Truelove
Vice President, Customer and Operations Excellence  |
|
From Data to Experience: Transforming the Consumer Journey at Michelin Consumer care is evolving, and Michelin is setting a new standard in pairing advanced analytics with human expertise. As a premium brand, Michelin demands a premium consumer experience that anticipates needs and caters to personalized consumer situations. Through innovative technology from IntouchCX and Michelin, agents are empowered with real-time knowledge prompts, surfacing critical information for complex or uncommon scenarios. Combined with AI-driven roleplay and adaptive training, this approach equips agents to operate beyond rigid scripts, balancing autonomy with precision. This also provides the groundwork for better Voice of the Consumer reporting and CRM predictive insights to guide future personalized journeys without overcommunication. Key takeaways:
This session will feature an interactive breakout exercise, giving participants the opportunity to experience the workshop concepts firsthand and apply them in a collaborative setting. Thanks to Our Partner
|
|
How Peloton Fixed Its MSAT Headache Peloton was facing member experience challenges across its global partner network. To fix this problem, Peloton did what any great brand would do: they hit the reset button. The result? A laser-focused turnaround on their new north star metric: MSAT. Join this session to see how Peloton and ibex:
If you want to see how one of the world’s most recognizable brands turned MSAT from a pain point into a proof point, don’t miss this Moment of Brilliance. Thanks to Our Partner
|
|
From Transformation to ROI: Lessons from CX Leaders The contact center is at a turning point—leaders are under pressure to deliver efficiency without eroding the customer experience. In this Shop Talk, Todd Stanley, former COO of Achieve and former senior CX leader at Intuit, will share candid lessons from years of leading large-scale transformations. Drawing on his experience deploying enterprise AI, Todd will discuss how organizations can:
In this session, we’ll explore what’s next for contact centers as AI Agents move from concept to reality, reshaping how routine work is handled and how human expertise is elevated. Leaders will gain perspective on how to prepare their organizations today to capture these opportunities tomorrow. Thanks to Our Partner
|
|
The AI Menu in Action: Reimagining the Customer Journey with AI at Every Phase AI has the potential to transform every touchpoint of the customer journey, but only if leaders know where and how to apply it for measurable impact. In this highly interactive session, you’ll work alongside fellow CX decision-makers to identify critical challenges across the pre-interaction, interaction, and post-interaction phases. Using “The AI Menu” as a framework, you’ll explore real-world examples, from AI Receptionists and Intelligent Virtual Agents that predict customer needs to AI-powered analytics that uncover post-call insights, and co-create targeted, AI-driven strategies to overcome these challenges. You’ll leave this session with actionable opportunity statements, fresh perspectives from your peers, and practical tools to integrate AI across your customer engagement processes. Whether you’re optimizing the moments before a customer ever speaks to an agent, enhancing live interactions with real-time intelligence, or using post-call insights to drive continuous improvement, this session will equip you to design seamless, impactful customer experiences powered by AI at every phase. Thanks to Our Partner |
 Glen Tillman
Senior Director Product Marketing |
|
Next-Gen Agent Onboarding: How Reddy and Morgan & Morgan Transformed Training Outdated training tools are failing modern customer service agents—leaving them underprepared, under-coached, and overwhelmed. In this interactive Shop Talk, Reddy invites you to step into the shoes of a newly hired agent navigating legacy onboarding and the daily grind of frontline support. Through hands-on simulation, reflection, and role-play, you’ll uncover the gaps in traditional enablement and see why it’s time to get your LMS truly “Reddy” for your agents. Key Takeaways:
Thanks to Our Partner
|
|
Building Empathetic Voice AI: Architecting Real-Time Conversations at Scale What makes a voice AI experience feel genuinely human? It’s not just about getting the words right. It’s about understanding tone, intent, and emotion in the moment, and responding in a way that builds trust. Behind every seamless voice experience is a complex orchestration of intent recognition, sentiment analysis, and real-time decisioning. This workshop takes you inside the engine of a truly AI-native voice platform where you’ll explore how LLMs, NLU, and proprietary tuning come together to create voice agents that actually feel human. Through a live product demo, you’ll see what’s possible when empathy meets engineering. This workshop will explore:
Thanks to Our Partner
|
|
Pilot with Precision: Aligning Generative Agent Pilots to Risk Tolerance and ROI Launching a generative AI pilot is easy. Launching the right one—one that aligns with your risk tolerance, delivers measurable outcomes, and sets you up to scale—is far more difficult. Presented by ASAPP and PTP, this session will help CX leaders to choose, test, and take generative agent pilots to the next level, with confidence. You’ll explore:
If you’re looking to quickly accelerate your AI journey and maximize ROI—without overpromising or overengineering—this session is for you.
|
|
How AI Is Powering the Next Wave of Omnichannel Customer Service Today’s customers don’t think in channels. They expect fast, personalized support, wherever they are. From chat and social to messaging apps, email, and phone, customer service is now omnichannel. But with this flexibility comes a new challenge: delivering consistent, contextual, and cost-effective service at scale. In this session, Freshworks will explore how AI is transforming customer support across every channel, not by adding more tools, but by making every interaction smarter. Through a live demo and collaborative discussion, they’ll break down how Freddy AI works across chat and email to resolve common queries, empower agents with insights, and simplify tool complexity. You’ll get a practical look at how it all comes together, including:
Attendees will leave with clear strategies for scaling intelligent support without sacrificing the human touch.
Thanks to Our Partner
|
|
TripAdvisor’s Playbook for AI That Gets 5-Star Reviews: How to Avoid the Implementation Mistakes That Break Customer Experience You’ve seen the pattern: AI projects that start strong, then somehow make everything more complicated. What looked like a quick win turns into months of integration headaches, frustrated teams, and executives asking uncomfortable questions about ROI. TripAdvisor made this exact mistake. Then Tim Barker and his team developed a holistic approach that transformed their entire customer support operation—dramatically improving resolution times while reducing costs and boosting agent satisfaction. In this hands-on session, Tim and Laivly’s Matt Bruno will walk you through the same methodology that delivered these results. What You’ll Experience Real-World Case Study Strategic Framework Deep-Dive Interactive Workshop Walk out with your personalized AI workflow map and phased implementation plan.
Thanks to Our Partner
|
|
RingCentral, Inc. (NYSE: RNG) is a leading provider of AI-driven cloud business communications, contact center, video and hybrid event solutions. RingCentral empowers businesses with conversation intelligence, and unlocks rich customer and employee interactions to provide insights and improved business outcomes. For more information, visit: ringcentral.com . |
|
Powered by purpose, TELUS Digital leverages technology, human ingenuity and compassion to fuel remarkable outcomes and create inclusive, thriving communities in the regions where we operate around the world. Guided by our Humanity-in-the-loop principles, we take a responsible approach to the transformational technologies we develop and deploy by proactively considering and addressing the broader impacts of our work. Learn more at: telusdigital.com |
 ibex delivers innovative BPO, smart digital marketing, online acquisition technology, and end-to-end customer engagement solutions to help companies acquire, engage and retain customers. ibex leverages its diverse global team and industry-leading technology, including its AI-powered ibex Wave iX solutions suite, to drive superior CX for top brands across retail, e-commerce, healthcare, fintech, utilities and logistics. ibex delivers innovative BPO, smart digital marketing, online acquisition technology, and end-to-end customer engagement solutions to help companies acquire, engage and retain customers. ibex leverages its diverse global team and industry-leading technology, including its AI-powered ibex Wave iX solutions suite, to drive superior CX for top brands across retail, e-commerce, healthcare, fintech, utilities and logistics.For more information, visit: www.ibex.co |
|
Chad McDaniel Chad McDaniel is a well-known advocate for the Customer Management Executive. He works tirelessly to showcase the success of today’s Customer Executive. Execs In The Know believes that advancements in customer success are created when leaders share experiences, outlooks and insights – “Leaders Learning From Leaders.” Our mission is to provide measurable value to the corporate customer executive, by delivering customer experience improvements, in an efficient and effective manner. Execs In The Know connects customer professionals to valuable content, thought leadership, industry insight, peer-to-peer collaboration and networking opportunities. We support the customer professional in a live format by hosting national events (Customer Response Summit) and conducting a series of Executive Think Tanks. |
|
Andy Watson Andy Watson is the Senior Product Marketing Manager for RingCentral’s CX portfolio. Prior to joining RingCentral, he held UCaaS and CCaaS Product Marketing roles at Broadvoice and Mavenir. Additionally, he has extensive telecom experience with Nortel Networks, Ericsson, and GENBAND (now Ribbon Communications), serving in various roles in Technical Documentation, Program Management, and New Product Introduction. |
|
Alex Avery Alex Avery is a product leader at Sierra, where he partners with customer experience teams at innovative brands to deploy AI agents that elevate support operations and drive better customer outcomes. With a focus on practical AI integration, Alex helps companies accelerate automation without compromising on service quality. His recent work includes leading successful deployments for brands like Minted and Pendulum, where Sierra’s agents now handle a wide range of customer interactions across chat, email, and voice channels. Prior to Sierra, Alex cofounded Mainstreet AI, a product development firm which helps companies accelerate their adoption of AI, and Gather, a software platform for museums and universities to manage their member experience. |
|
Flip It Live: How Belk Launched Voice AI in Record Time Why talk about launching AI when you can watch it be deployed in minutes? In this interactive session, you’ll see a real retailer, Belk, set up Flip’s Voice AI from scratch to fully operational in minutes, proving what most vendors call “impossible.” Belk’s Senior Director of Customer Experience, Jessica Patel, joins Flip’s Co-Founder and Chief Revenue Officer, Sam Krut, and Vice President of Demand & Partnerships, Shawn Li, to share how the 137-year-old retailer replaced its IVR with a modern Voice AI experience and went from first conversation to launch in only 74 days. They’ll reveal early results from successfully putting customer-facing AI on phones without a long, custom, expensive build, and the early results Belk is seeing in its most important channel. Join this session for laughs, learnings, and a guide for how your brand can launch Voice AI, too. You’ll see and hear:
Watch a brand “flip the script” on phone-channel CX and walk away with a practical roadmap to launch Voice AI.
Thanks to Our Partner
|
|
Unlocking Call Center Revenue: How Princess Cruises is Driving Growth Most call center agents spend more time figuring out who to call or what to say than actually talking to guests. Princess Cruises is flipping that model — using AI and real-time data to put the right leads, the right insights, and the right timing directly into agents’ hands, making their jobs easier and more rewarding. Join Alvin Stokes, VP of Global Reservation and Guest Services at Princess Cruises, and Scott Sahadi, CEO of harpin AI, as they reveal how new tools are helping agents close more bookings with less guesswork. You’ll learn how Princess Cruises is:
This isn’t about more calls. It’s about smarter calls that convert — faster. If you want to see what significant MoM revenue growth looks like in action, don’t miss this.
|
|
Transforming Your Contact Center into a Modern Resolution Engine For too long, themes in CX have been focused on deflection, asking, “How many customers can we avoid?” The more meaningful question is: “How can we resolve their issues?” Customers don’t care how many steps you eliminated in your workflow or how much faster your team completed their post-call dispositions. They care about one thing: Was my problem solved quickly and effectively? As CCaaS continues to evolve, contact-center leaders must meet ever-higher demands for efficiency, personalization, and seamless omnichannel service. Teams can no longer tolerate half-baked channels, siloed agents, or reporting nightmares. Today, they’re embracing AI-powered, unified workspaces that weave rich contextual data with intelligent, empathy-driven tools so every interaction becomes fast, personal, and on-brand at scale. In this session led by Zendesk, you’ll explore real-world examples of contact centers around the world that have:
You’ll walk away with actionable strategies to transform your contact center into a modern resolution engine by:
Thanks to Our Partner
|
|
Designing the Modern Contact Center Experience: Human + AI Collaboration, Omnichannel Orchestration, and Voice Platform Transformation As customer expectations evolve and AI continues to reshape service delivery, contact centers must transform into agile, intelligent experience hubs. This forward-looking workshop explores how to design the modern contact center by integrating the best of human empathy, agentic AI, and omnichannel strategy. Participants will dive into how to orchestrate seamless journeys across voice, chat, email, and social, creating consistent experiences regardless of channel. We’ll explore how to modernize legacy systems and elevate voice platforms through next-generation IVR (NGIVR) and agentic AI that empowers agents and streamlines customer interactions. A key focus will be on Human + AI collaboration: learning how to optimize handoffs between bots and humans, design emotionally intelligent experiences, and deploy next-gen agent assist tools that elevate frontline performance. Through practical frameworks, real-world case studies, and collaborative exercises, attendees will leave with a better understanding of:
A must-attend session for contact center leaders focused on delivering measurable, strategic value through every customer interaction. Thanks to Our Partner
|

Sierra is the platform that helps businesses build better, more human customer experiences with AI. Founded by industry veterans Bret Taylor and Clay Bavor, Sierra enables companies to deploy autonomous AI agents that provide fast, personalized, always-on support across channels. Trusted by brands like SiriusXM, Sonos, and ADT, Sierra’s flexible model meets customers where they are—offering everything from enterprise-ready, fully supported deployments to build-your-own no-code journeys. Both CX and Engineering teams can move fast, choosing the right approach to fit their evolving needs. For more information, visit: sierra.ai |
|
The Human Advantage: Why People Still Power Great CX in the Age of AI In an era dominated by AI and automation, it’s easy to lose sight of what’s most critical in delivering standout customer experiences: the people making them happen. Amid the tech-driven transformation of CX, one truth remains—companies that thrive are those where agents, and the teams supporting them, are engaged, empowered, and equipped to deliver at a high level. In this dynamic session, Terri DeMent, Director, Consumer Engagement at Nestlé Purina—and Amy Bouthilet, VP of Global Talent at Alta Resources, a leading end-to-end CX BPO, discuss what it truly takes to build and sustain an employee-first culture. Drawing from real-world examples, they’ll share the challenges and breakthroughs of scaling engagement across complex enterprises, and how placing people at the core of CX operations leads to measurable impact—from improved customer satisfaction scores to stronger revenue performance. With a 9-year partnership with Gallup, Alta’s proven approach to employee engagement and leadership development has redefined how to embed culture into the everyday fabric of CX delivery. Attendees will gain actionable strategies to overcome barriers, develop engaged teams, and elevate both employee and customer outcomes in a world increasingly shaped by technology. Key Takeaways:
Join us to discover why, amid rapid technological change, people still drive CX success.
|
|
A Masterclass in CX Technology Sourcing Choosing the right customer experience (CX) technology partners isn’t just a procurement decision—it’s a strategic one. From discovery to delivery, the way you source, evaluate, and manage technology solution providers can make or break your ability to deliver seamless, high-impact customer experiences. In this expert-led panel, seasoned CX leaders will guide you on techniques to find and evaluate the best providers to deliver on your business requirements. You’ll hear real-world examples and gain practical tools for maximizing value from your technology partnerships while staying agile in a fast-evolving digital landscape.
Whether you’re looking to optimize current vendors or source new technology, this panel will offer a blueprint for smarter, more strategic CX technology decisions.
|
|
Reality Check: Are AI & Automation Living Up to Their Promise in CX AI and automation are no longer emerging tools; they’re embedded in the DNA of today’s CX strategies. From transforming contact centers to driving operational efficiency and delivering more seamless customer interactions, they’ve promised smarter, more seamless customer experiences. But are they delivering? This panel takes a clear-eyed look at what’s really happening after implementation. What gains have proven sustainable? Where are expectations falling short? And how are CX leaders rethinking their approach as they face the hard truths of integration, training, measurement, and impact? You’ll hear from leading brands on navigating the evolving balance between humans and machines, including how they’re redefining agent roles, capturing the right metrics, and translating the voice of the customer into iterative, AI-fueled improvements. Whether you’re scaling automation or just beginning to integrate AI pilots, this session offers grounded insights, honest lessons, and forward-looking guidance for building the intelligent contact center of tomorrow. Thanks to Our Partner
|
|
CX Livewire: Polling, Predictions, and Instant Feedback This fast-paced session brings together a panel of CX leaders who are deeply immersed in the challenges and opportunities facing the industry today. Drawing on their diverse backgrounds and day-to-day leadership, panelists will explore what’s driving progress, what’s standing in the way, and how leading organizations are turning insight into impact. Attendees will walk away with a clearer view of the CX landscape, real-time benchmarking from peer responses, and fresh strategies they can apply within their own teams. By pairing live polling with Execs In The Know’s latest research report’s core findings, we’ll use the session to test predictions, validate (or challenge) existing data points, and capture what’s changed in real-time. This approach gives attendees a rare opportunity to see how their organization stacks up, where their peers are headed, and what strategies are gaining traction across industries right now.
Thanks to Our Partner |
|
The Talent Shift: Hiring, Training, and Compensation in an AI World Customer expectations aren’t the only thing evolving, so are the people behind every interaction. As AI and automation continue to reshape the contact center, they’re not just enhancing tools and workflows; they’re fundamentally transforming the agent role itself. In this new era, agents are expected to do more than follow a script. They’re problem solvers, brand ambassadors, and emotional first responders—navigating increasingly complex issues that require both high-tech fluency and high-EQ finesse. These changes are pushing organizations to rethink everything: how we recruit and train, how we compensate and support, what skills matter most in the modern CX workforce, and how entirely new roles may emerge. This panel brings together CX leaders to unpack how AI is reshaping the future of work: redefining the skills we hire for, influencing compensation models, and transforming how training, reskilling, and upskilling are delivered and absorbed. As the role of the agent evolves—shifting from repetitive tasks to higher-value, empathy-driven work—companies must balance automation with human augmentation and adopt strategies for building and supporting a workforce prepared to meet the demands of a more complex, tech-integrated customer experience. The future is faster, smarter, and more connected but success depends on leading with intention, investing in emotional intelligence, and designing roles that elevate both technology and humanity.
Thanks to Our Partner |
|
Board Panel: The Signals We’re Missing In a world flooded with dashboards and metrics, the loudest signals often steal the spotlight—while the most powerful insights go unheard. This panel explores what it means to truly listen to the silent majority of customers: those whose feedback isn’t captured in traditional surveys, whose experiences are filtered through cultural bias, or whose voices are lost in outdated listening systems. Join the EITK Advisory Board as they challenge the current state of customer listening by asking hard questions:
We’ll also explore how AI-powered sentiment detection can help uncover unspoken truths and emerging emotions—if applied with intention and ethics. From tuning into passive signals to reshaping how and where we listen, this conversation will open new possibilities for creating a listening culture that is inclusive, intelligent, and alive. If we want to meet customers where they are, we must hear even what they don’t say. The future of customer experience depends not just on collecting more data—but on listening differently.
|
Incorporating various technologies and working alongside outsourcers produces the best outcomes when alignments are in place and all parties are in sync. Without these synergies, brands risk inefficiencies across their operations. This session will explore how Ulta, in collaboration with IntouchCX, leverages innovation to shape its technology roadmap, enhance insights and analytics, and optimize workforce planning. The discussion will focus on how strategic sprints, integrated solutions and automation can drive efficiencies. This session will highlight real examples, showcasing how transparency, collaboration, and automated workflows have fostered positive change.
The modern CX landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by the convergence of emerging technologies such as AI, advanced data analytics, and human emotional intelligence (EI). This “AI-Human Alliance” represents a transformative opportunity for organizations to deliver exceptional CX at scale — personalized, accurate, compassionate and profitable.
This is an interactive workshop where we’ll explore how to unlock the power of human interaction through technology to boost satisfaction, streamline processes, and empower employees to deliver faster, more personalized, and emotionally intelligent interactions.
Key takeaways:
- AI-powered strategies: Optimize processes, enhance customer experiences, and drive efficiency through the AI-Human alliance.
- Empowered workforce: Leverage AI to resolve complex issues, foster customer loyalty, and drive growth through predictive insights, personalization, and process automation.
- Scalable, agile operations: Design a CX model that balances technological innovation with human ingenuity for your organization’s competitive edge.
Join us for this hands-on session that will reshape how you think about AI, operations, and customer service—leaving you with actionable strategies to drive real impact.
Traditional customer research captures moments in time, but customers experience brands over months and years. What if you could continuously capture authentic customer stories as they unfold, revealing hidden pain points and opportunities that surveys and focus groups miss?
This hands-on workshop introduces a transformative approach to customer understanding: creating a living library of real-world experiences that evolves alongside changing customer needs. Through video diaries, longitudinal tracking, and AI-powered analysis, organizations can move beyond point-in-time data to understand the Total Experience in real time.
Through interactive exercises and real-world examples, you’ll learn how to:
- Build rich video repositories capturing authentic customer interactions
- Identify emerging trends and friction points before they appear in traditional metrics
- Transform ethnographic insights into actionable CX improvements
- Use AI to analyze thousands of customer moments and surface meaningful patterns
- Design a continuous customer listening program that reveals unmet needs
- Create feedback loops that drive rapid CX optimization
- Build internal support for ethnographic research approaches
- Connect customer stories to business outcomes to drive revenue growth and retention
Workshop Outcomes:
- Tools for identifying key customer moments to capture and analyze
- Strategies for translating ethnographic insights into measurable CX improvements
- Methods for communicating the business impact of longitudinal research
- Templates for crafting compelling customer stories that drive organizational change
- An action plan for shifting from periodic to continuous customer research
Join us to explore how continuous ethnographic insights can transform your CX strategy and create deeper customer relationships.
The hype around generative AI’s (GenAI) potential to transform customer experience is real. And so is the potential for it to create meaningful lift and impact for businesses. The catch is that it’s not a one-size fits all approach and GenAI is most effective when housed within structured business processes. Join NLX Chief Customer Officer Christian Wagner and Field CTO Josh Schairbaum for a discussion that unpacks how GenAI can deliver the most value for enterprises.
We will explore strategies for how to apply GenAI to customer-facing use cases, strategies for identifying the best use cases to start with, and go under the hood to show attendees how to build a workflow that taps the GenAI within your structured business processes.
You wouldn’t use a hose to build a desk, just as you wouldn’t rely on a shark as an emotional support animal. Having the right tool for the job is crucial—so why do so many companies still rely on PDFs for their knowledge management system?
Join Atlanticus and livepro for an insightful discussion on how one company transitioned to a more effective Knowledge Management System and the transformative impact it had on their operations. We will walk you through their journey, including the challenges faced, key learnings, and measurable results. By the end of this session, you will gain actionable insights into how a premier Knowledge Management Solution can drive efficiency, enhance customer experience, and future-proof your organization.
Key Takeaways:
- Common pitfalls of ineffective knowledge management systems
- Why Atlanticus chose livepro to overcome these challenges
- The measurable impact of livepro’s implementation on efficiency and customer service
- Successes and challenges encountered during the transition
- How integrations with other tools amplified positive outcomes
- The surprising role of a good mascot
- The evolving relationship between AI and Knowledge Management and its impact on the future of customer service
Discover how Mosaicx and Bank OZK have partnered for over four years to continuously modernize their customer experience. In this mini case study session, you’ll learn how Bank OZK transitioned from a legacy IVR system to an AI-powered Intelligent Virtual Agent, now known to customers as Ozzy. Since implementation, Bank OZK has achieved significant improvements in customer interactions, boasting a +4% year-over-year increase in containment and consistently streamlining their operations for both general business and local branches.
Attendees will gain insights into:
- The strategies behind Bank OZK’s successful migration to AI-driven customer interactions.
- How end-to-end call analytics unlock deeper insights into customer interactions to drive greater automation and adoption as well as predictive intent within and beyond Bank OZK’s IVA.
- Real-world lessons on scaling AI capabilities for sustained growth and improved customer satisfaction.
Traditional Learning Management Systems (LMS) have been a cornerstone of employee training for years, but they often fail to keep pace with the fast-changing demands of today’s CX teams. Too often, these programs turn into check-the-box exercises, delivering little value and falling short of creating real impact.
In this session, Reddy’s CEO and Harte Hanks reveal how they reimagined CX training by developing a next-generation program built on AI-driven simulations, continuous learning, and applied skill development. By revamping the curriculum for a Fortune 500 client, they created a transformative solution that not only elevated agent performance but also delivered superior customer outcomes and a better overall agent experience.
Discover how this innovative approach redefined Harte Hanks’ training strategy—reducing ramp time, cutting average handle time (AHT), improving call quality, and empowering agents to excel in dynamic, high-pressure environments.
CX Leaders understand AI’s impact on helping customers, but there are important choices to navigate. Should you invest a lot of time and resources in custom-building a solution, or should you take an afternoon to launch it and help customers immediately? Speed to operation matters, and adopting AI that impacts CX doesn’t have to be a long, complex process.
Flip has powered ninety percent of successful Voice AI deployments by retail eCommerce brands. In this live session, you’ll get hands-on experience as Flip enables a retailer to quickly integrate and deploy Voice AI — in one afternoon. Witness instant automation and implementation, with customer experience improvements from Day 1.
Attendees will:
- Hear Flip’s Voice AI in action as it interacts with a caller and resolves a real-time support issue.
- Learn how Voice AI can enhance customer experience metrics while reducing costs.
- Discuss how Voice AI can transform your phone channel into a revenue-generating asset.
Quality assurance is an important part of every great CX strategy, but reviewing 100% of agent-customer conversations across every channel is an impossible task – until now.
It’s time to take the guesswork out of quality assurance and let AI do the heavy lifting. During this session, you’ll see practical, real-world examples of how automated QA reduces customer churn, saves time and resources, and pinpoints agent training needs, all while boosting service quality and customer satisfaction. You’ll leave with the knowledge and tools needed to leverage automation for a competitive edge, along with real-life stories and data to back it all up.
Key takeaways include:
- How automated QA tools improve the customer and agent experience
- Practical strategies for implementing automated QA
- A look at reporting tools to help you gain insights and review performance trends
- Case studies of organizations already realizing the benefits of automated QA
AI is evolving fast, and CX leaders are under pressure to take action and deliver real results — all while navigating legacy systems, upskilling teams, addressing privacy concerns, and sifting through an overwhelming number of solutions to separate real value from hype. AI initiatives risk losing momentum without a clear, strategic roadmap before they create meaningful impact. In this interactive session, you’ll walk away with actionable strategies to define, fund, and execute an AI-powered CX strategy that drives tangible results in your business. By designing your own AI Success Roadmap aligned with your unique goals, you’ll be equipped to secure stakeholder buy-in and lead transformative CX outcomes.
Join Alvin Stokes, VP of Global Reservation and Service Operations at Princess Cruises, and harpin AI’s CEO, Scott Sahadi, as they reveal how a data-driven transformation reshaped Princess Cruises’ call center operations, improved guest experiences, and unlocked revenue opportunities.
Working together, they realized that prioritizing data quality and enhancing Princess’ data pipelines could significantly boost ROI—an often neglected challenge.
By improving data accuracy, integrating systems, and equipping agents with real-time insights and tools, they transformed these improvements into tangible results: reducing churn, lowering costs, and strengthening customer loyalty through personalized services.
Princess Cruises turned customer data quality from an overlooked challenge into a strategic advantage, enabling a successful omnichannel approach that delivered seamless service across customer touchpoints.
During this session, Alvin and Scott will discuss:
- How to fix fragmented data and start your customer data hydration journey.
- How to leverage observability and data science to investigate data quality issues.
- How to implement key initiatives that reduce costs and drive revenue growth.
- How to use data-driven insights to improve retention, reduce service costs, and enhance guest experiences.
- How to integrate disconnected systems and eliminate inefficiencies while maximizing existing investments in people, processes, and technology.
This transformation gave Princess the visibility it had been missing—turning an invisible problem into one they could track, understand, and resolve. Don’t miss this opportunity to hear from industry leaders about the strategies behind their success.
Join us for an insightful roundtable discussion on Turo’s AI adoption journey and the transformative impact on customer support operations. Jerry Howe, VP of Customer Support at Turo, and Dave Sheridan, VP of Sales & Marketing at Laivly, will share how Turo implemented AI using a structured “walk-run-fly” methodology—starting with AI-powered transcription and insights, scaling into real-time agent guidance, and laying the foundation for automation and quality assurance.
Discover how Turo leveraged AI to scale customer support while maintaining quality, improve agent decision-making, and streamline workflows. Learn how their phased approach enabled a smooth transition from AI-driven insights to automation, driving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
In this discussion, you’ll gain practical tips on:
- Walk – Using AI-powered transcription to capture conversation insights and enhance documentation
- Run – Implementing real-time agent guidance and automated case notes to improve decision-making
- Fly – Leveraging AI-driven automation and quality assurance to boost operational efficiency and customer experience
Designed for CX leaders, AI decision-makers, and contact center strategists, this session will provide actionable insights into simplifying AI adoption while maximizing its impact. Whether you’re just beginning your AI journey or looking to scale, you’ll leave with a roadmap for success.
Transform fragmented customer journeys into seamless experiences by starting with design and ending with technology, not the other way around.
For years, customer support organizations have navigated waves of technological change—from on-premise to cloud, from human agents to bots, and now the rise of AI. But too often, companies have taken a “lift-and-shift” approach, layering new tools onto old processes. The result? Fragmented experiences and mounting technical debt —frustrating both customers and stakeholders.
It’s time for a reset. In this session, COPC will introduce a proven framework for building AI-native customer journeys with purpose. Learn how to break free from outdated systems, align people and processes with technology, and create experiences that are intuitive, connected, and future-ready. Experts bring real-world examples to life, offering a clear path to designing seamless, AI-enabled customer experiences from day one.
In this discussion, you’ll learn how to:
- Design with intention—begin with the journey, not the tools.
- Eliminate legacy constraints with AI-powered solutions that reduce technical debt.
- Measure and refine customer experiences with a continuous improvement approach.
- Engage with peers in an open discussion on challenges, successes, and strategies for CX transformation.
- Apply a practical framework to align people, processes, and technology for end-to-end AI-native experiences.
This session is for CX leaders who are ready to move beyond incremental fixes and reimagine customer journeys with purpose and innovation.
An engaging session featuring real-world success stories from global leaders, Google and Sony PlayStation, in partnership with Limitless. This session will showcase how these iconic brands are leveraging GigCX, through empowering brand ambassadors, to deliver unmatched flexibility, scalability, and customer satisfaction. Attendees will gain exclusive insights into the results achieved, challenges overcome, and how to adopt GigCX. You will have the opportunity to engage in Q&A with industry leaders, gaining firsthand advice to apply to your own organization.
Customer experience leaders often face a familiar challenge: gathering valuable insights through surveys but struggling to see those insights turned into meaningful, client-centric actions. Even when business partners express interest, the outcomes often miss the mark of truly serving the client’s needs. At KeyBank, the CX+EX team operates with a clear and ambitious mandate—to ensure clients’ voices are not just heard but reflected in every experience the brand delivers.
In this keynote, Era Ziroe, Senior Vice President, Enterprise Client & Employee Experience Director, KeyBank, will take you behind the scenes of KeyBank’s innovative approach to CX management. She’ll share how her team’s unique structure and collaborative methods are reshaping the way insights are actioned upon, ensuring client needs drive decision-making and business outcomes. Learn how KeyBank leverages empathy, insights, and proactive collaboration to meet—and exceed—client expectations.
Join Era to discover how KeyBank’s CX team’s model is setting a new standard for delivering both business success and exceptional customer experiences. Don’t miss this opportunity to gain actionable strategies to elevate your CX practice.
Discover how global powerhouses Google and Sony PlayStation are revolutionizing customer experience through GigCX in collaboration with Limitless. In this dynamic session, you’ll hear firsthand how these brands are harnessing the power of freelance brand ambassadors to drive unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and customer satisfaction. Gain exclusive insights into their successes, the obstacles they’ve overcome, and practical strategies for implementing GigCX in your own organization. Plus, engage in a live Q&A with industry leaders to get expert guidance tailored to your business needs. Don’t miss this opportunity to stay ahead in the evolving customer experience landscape!
Come see how the World’s Leading AI Simulation Coaching company has brought Generative AI to life for your frontline team members. You’ll see for yourself why they can’t get enough of their personal AI Coach.
It’s no mystery that repetitive practice produces consistent results. Providing that hands-on learning for both new hires and tenured associates at scale without technology is unreasonably expensive, inefficient, and nearly impossible. Zenarate’s AI Coach allows companies worldwide to overcome each of these challenges.
If you want to learn how leading brands have delivered the following results with AI Coaching…
- Improved speed to proficiency by 70%
- Reduced attrition by 52%
- Cut training expenses by 50%
- Improved conversion rates by 34%
- Increased QA + CSAT by 47%
…then don’t miss this interactive innovation session delivered by Learning & Development expert Casey Denby.
Come experience AI Coach for yourself.
As AI automates routine tasks like FAQs and simple requests, customer service agents are increasingly vital for handling complex, high-emotion interactions that require empathy, critical thinking, and problem-solving. This shift demands hiring for emotional intelligence and communication skills, along with the ability to collaborate with AI tools.
Training must adapt to prepare agents for hybrid roles, where they enhance human interactions through AI support. As agents take on more specialized, high-impact tasks, compensation must reflect their growing importance as brand ambassadors. Organizations must rethink hiring, training, and retention to ensure agents are both technically and emotionally prepared to excel in an AI-enhanced landscape.
Travel has always been about people — but as technology and innovation reshape the journey, how do we ensure the human touch remains at its heart? Keynote Alvin Stokes, Vice President of Global Reservation and Service Operations Guest Services at Princess Cruises, shares his journey of transforming guest experiences through the power of data science and machine learning.
Learn how Princess Cruises overcame systemic challenges, improved data quality, and leveraged cutting-edge tools from Harpin and Salesforce to deliver contextually relevant, personalized interactions to guests. From wearable technology that elevates onboard experiences to agent-facing personalization tools that empower meaningful customer connections, Stokes will reveal the strategies behind the premium cruise brand’s 20% improvement in operational efficiency/budget and customer satisfaction.
Discover the untapped potential of data science, the importance of data quality in achieving personalization at scale, and real-world case study insights into creating seamless, always-on engagement. Whether it’s mapping the customer journey, fostering loyalty through data-driven insights, or balancing technology with human-centered service, this keynote explores the intersections of possibility that drive CX excellence.
In the dynamic world of hospitality, staying ahead requires unwavering dedication to continuous improvement and the embrace of a growth mindset. Join Frid Edmond, Senior Vice President of Global Customer Engagement Centers at Marriott International, in her transformative talk on “Leading Innovation and Change,” focusing on the strategies and leadership needed to foster innovation and growth.
In her keynote, Frid will share insights from her remarkable journey of leading teams through transformational change. She will reveal how she masterfully integrated loyalty programs after a large-scale merger, realigned organizational structures, and spearheaded technological advancements at a Fortune 500 company. Her insights will illuminate a range of innovative strategies and approaches, demonstrating how to navigate and implement these significant changes to achieve organizational success.
Attendees will gain invaluable insights into the leadership principles driving transformation. This session will spotlight the power of a “growing forward” mindset—encouraging continuous learning, adaptability, and proactive problem-solving to help individuals shift from resistance to resilience. Key themes include Courageous Leadership: making bold decisions and taking calculated risks; Persistence: overcoming obstacles and staying committed to long-term goals; and Resilience: adapting and thriving in the face of challenges.
Explore how these strategies can be applied to your organization, driving sustainable growth and positioning your business for long-term success. Whether you’re looking to enhance your organizational capabilities or lead your team through transformative change, this keynote will provide the inspiration and tools you need to thrive in an ever-changing market.
In an era of rapid innovation and evolving customer expectations, transforming your organization to meet the needs of customers is critical. Join keynote speaker Christie Sandoval, Senior Vice President of Consumer Experience at T-Mobile US, as she shares how T-Mobile, one of the largest telecommunications companies in the U.S., is integrating the power of technology with human touch in their mission to deliver the best customer experiences possible.
With people at the heart of day-to-day customer interactions, Christie emphasizes the importance of empowering employees with AI technology and superpowers to ultimately uplevel and elevate the customer experience. This requires consistently assessing and anticipating customer needs and an inside-out, people-first approach to effectively operationalize change, foster a customer-obsessed culture, and collectively push the status quo.
Christie leads over 15,000 employees across the U.S. – the highest-ranked, most-awarded customer service team in the industry. She is deeply passionate about fuelling a culture where employees can be their most unique selves, grow personally and professionally, and do their best work. Her keynote will provide invaluable insights into how T-Mobile’s unique E2C (employee-to-customer) approach, powered by technology and data, translates to human-centric customer experiences.
In 2023-2024, Spirit Airlines embarked on a major brand overhaul for Guest Care, creating the perfect opportunity to elevate its Guest experience. Vanessa Hardy-Bowen, Director of Guest Care & Contact Centers at Spirit, had already been leading efforts to integrate AI into the airline’s customer service operations. The brand transformation provided a pivotal moment to implement her vision of a cutting-edge, AI-powered contact center.
In this case study, Vanessa will walk you through Spirit Airlines’ AI journey—from identifying the right solution with her technical team to overcoming challenges like a failed AI voice pilot and addressing security concerns around generative AI. You’ll gain valuable insights into the airline’s approach to enhancing guest interactions and the results they’ve achieved so far.
Key takeaways for attendees:
- Strategies for aligning stakeholders and building a cross-functional team, including IT
- An overview of AI options for customer experience, along with their benefits and limitations
- Tips for managing stakeholders with differing priorities
- Factors to consider when choosing between a phased AI adoption or a full-scale implementation, including channel strategies
- Essential metrics to measure and understand AI agent performance
Join Vanessa to learn how Spirit Airlines is shaping the future of customer experience through AI.
In today’s customer-driven market, companies are increasingly leveraging data to craft compelling Customer Experience (CX) stories that resonate with consumers. Businesses can gain deep insights into customer preferences, pain points, and expectations by harnessing data from various touchpoints—such as customer feedback, behavioral patterns, social media interactions, and transactional data. This data-driven approach allows companies to create personalized and engaging CX narratives that reflect their commitment to understanding and meeting customer needs.
Through advanced analytics, organizations can visualize the customer journey, identifying key moments that shape perceptions and influence loyalty. By analyzing quantitative metrics (e.g., Net Promoter Scores, Customer Satisfaction scores) and qualitative insights (e.g., customer reviews, sentiment analysis), businesses can illustrate how they have evolved in response to customer feedback, showcasing improvements and successes in delivering exceptional experiences. Data allows for continually refining CX strategies, enabling companies to highlight their responsiveness, adaptability, and focus on long-term customer relationships. Ultimately, using data to tell a CX story not only strengthens brand credibility but also fosters trust and emotional connections, setting companies apart in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Explore how Artificial Intelligence is transforming the landscape of customer experience, not just through efficiency, but by creating deeper, more meaningful interactions. In this panel, we’ll dive into how AI tools like chatbots, recommendation engines, and sentiment analysis systems are being used to enhance empathy and personalize customer engagement. Learn how businesses are leveraging AI to build emotionally intelligent connections with customers, driving satisfaction, loyalty, and long-term relationships. Discover the future of AI as a catalyst for delivering humanized, impactful customer experiences.
CX Livewire: Polling, Predictions, and Instant Feedback is an engaging 30-minute experience where the panel turns the spotlight on the audience! The panel will introduce a key topic and ask poll questions to gather real-time audience feedback. Panelists will predict audience responses and then dive into a lively discussion to explore whether their predictions were spot-on or missed the mark. This interactive format offers a unique way to gauge audience sentiment and spark conversation around real-time insights—perfect for CX Leaders looking to stay ahead of emerging trends.
As AI automates routine tasks like FAQs and simple requests, customer service agents are increasingly vital for handling complex, high-emotion interactions that require empathy, critical thinking, and problem-solving. This shift demands hiring for emotional intelligence and communication skills, along with the ability to collaborate with AI tools.
Training must adapt to prepare agents for hybrid roles, where they enhance human interactions through AI support. As agents take on more specialized, high-impact tasks, compensation must reflect their growing importance as brand ambassadors. Organizations must rethink hiring, training, and retention to ensure agents are both technically and emotionally prepared to excel in an AI-enhanced landscape.
As customer experience evolves beyond digital transformation hype, organizations face complex decisions about where and how to invest in service excellence. This panel pulls together seasoned CX leaders to tackle pressing questions that directly impact business value and competitive advantage like:
- How are progressive leaders quantifying and communicating the true ROI of customer experience investments?
- Has the CX community become too focused on metrics at the expense of true customer advocacy? What capabilities are becoming more critical for service professionals in an AI-augmented environment?
Join members of the Execs In The Know Advisory Board, Lisa Oswald, Senior Vice President, Customer Service at Travelzoo; Pete Mallot, Worldwide Support Leader for Modern Life and Business Programs at Microsoft; Carolyne Truelove, Vice President, Reservations and Service Recovery at American Airlines, and Todd Sale, Senior Vice President, Customer Experience at Corpay, as they share their unique insights on where to invest, what to measure, and how to demonstrate CX’s direct contribution to business success.
In today’s dynamic business environment, organizations increasingly recognize the importance of effective support models and strategic partnerships to enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
This panel explores developing and implementing robust people and agent support systems, emphasizing the significance of well-designed partnerships between businesses and their support teams. Whether your organization leverages outsourced services or manages operations internally, navigating agent support requires strategic insight and adaptability.
Support models must stand ready to solve complex problems, drive digital transformation, and leverage technology to elevate the customer and employee experience. By fostering collaboration and leveraging the strengths of both internal and external resources, companies can build a support infrastructure that is both responsive and resilient.
This Panel Discussion will provide valuable insights into:
- Best practices for creating and maintaining partnerships that align with organizational goals.
- The value of strong comprehensive support models that can meet the evolving needs of businesses and their customers.
- Leveraging the tools and technology that can strengthen your agent delivery model.
- Join this conversation to learn how to navigate agent support and ensure better client, customer, and employee experiences.
You’ve implemented automated solutions but how well are they being operationalized to drive measurable results? Automation is impacting all facets of business and getting the most out of it requires experience and insights to successfully integrate it across your entire CX lifecycle.
Join Matt Wheatley, Chief Revenue Officer at IntouchCX and Ingrid Betts, SVP of Transformation and Strategy at Conservice for a deep dive on strategic automation integration and how it can impact the bottom line.
Key Takeaways:
- How to integrate AI & automation across your CX operations
- Identifying & enabling automation across the customer & agent journey
- Leveraging expertise in platform and tech stack integration
You can have both – improved CSAT and AI automatically answering support requests.
Discover how one of our clients is doing just that and how they:
- Gained leadership and team buy-in for AI-first customer service
- Prepped for and launched an AI Agent
- Optimize AI agent performance for their organization
- Improved CSAT at the same time
Whether you’re still preparing to adopt AI for customer support or want to improve your resolution rates, this session will provide you with specific tactics and concrete advice to successfully incorporate AI into your strategy.
Delivering exceptional customer experiences (CX) requires more than just implementing the latest technologies. It demands a holistic, long-term approach that transforms organizational culture and mindsets.
This session will examine strategies for creating a sustainable culture of CX transformation, where continuous improvement, agility, and customer-centricity become embedded in the enterprise’s DNA.
It will explore the key elements needed to drive lasting change, including:
- Leadership alignment
- Employee engagement
- Process optimization
- Data-driven decision-making to drive business value
In this case study presentation, we delve into the successful Mastercard CX journey, showcasing how they have transformed CX through a human-centered approach.
Key discussion points include:
- Mastercard’s digital transformation journey and the role of partners like TELUS International in supporting their vision.
- The importance of mastering foundational CX operations before implementing AI and other digital technologies.
- How Mastercard and TELUS International have balanced human and AI collaboration to enhance customer service.
- Specific examples of successful CX transformation.
- Insights and advice for CX leaders on leveraging AI – what it can and cannot do
Customer service leaders are under constant pressure to drive growth and customer satisfaction with innovative solutions. In this panel led by Freshworks, CX industry leaders will share critical insights and considerations they face when looking to drive rapid innovation in their organizations. They will discuss the critical foundations they focus on to ensure their innovation decisions drive the business results they seek and are future-proof.
You will gain insights into:
- The power of data in ensuring a unified view of your customer
- Embracing AI to drive scale, trust, and security
- Enabling key leader insights to drive accurate decision-making
Through engaging discussions and hands-on exercises, you will develop a clear understanding of the essential platform capabilities required to drive exceptional customer service and achieve specific business objectives. Sharpen your platform selection skills through interactive exercises designed to evaluate key capabilities and ROI, including:
- Developing a blueprint to unify customer data
- Creating a roadmap for AI deployment
- Identifying proactive, real-time KPIs
Don’t miss this opportunity to network with industry peers and gain actionable strategies to propel your organization forward.
The goal of this panel session is to explore how empathy and emotional intelligence (EI) can serve as transformative forces in customer experience (CX) management, transcending traditional metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) scores. In an era where customers expect more personalized and meaningful interactions, the integration of empathy and EI into CX strategies is becoming increasingly vital.
This session will feature a panel of subject matter experts (SMEs) who will share insights and real-world examples of how leading organizations are incorporating these human-centric approaches to enhance customer loyalty and satisfaction. Through interactive discussions, we’ll lean into challenges and opportunities associated with fostering an empathetic culture within CX teams and company culture.
CX leaders will leave with actionable ideas, compelling anecdotes, and valuable resources to guide the adoption of empathy-driven approaches in their own organizations. This session aims to inspire a shift from viewing customer interactions as mere transactions to embracing them as opportunities to build deep, emotional connections that drive long-term success.
As AI transforms the contact center, supporting people managers becomes critical. During this session, we’ll dive into empowering managers to thrive in this new era.
Join our session to learn how to:
- Foster decision-making and problem-solving by managers.
- Promote continuous learning for effective leadership.
- Leverage AI tools for data-driven coaching and personalized experiences.
- Balance automation with the human touch for empathy and success.
Through practical examples and interactive discussions, participants will gain actionable insights into creating an environment where agents and managers feel empowered, supported, and equipped to succeed in this new era of AI-driven contact centers.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, delivering exceptional customer experiences is more critical than ever. Join us for an in-depth session where we explore how Limitless, in collaboration with Google, has harnessed the power of GigCX to transform the way customer support is delivered.
In this session, we will delve into the innovative strategies that have placed customers at the heart of the customer experience, leveraging the flexibility and scalability of GigCX. You’ll discover how Limitless and Google have reimagined traditional customer service models, empowering gig experts to deliver personalized, empathetic support at scale, and in real-time.
This case study will provide actionable insights into how your organization can adopt similar approaches to revolutionize customer engagement, drive customer satisfaction, and ultimately, foster deeper brand loyalty by putting the customer first in every interaction. Don’t miss this opportunity to learn from industry leaders and take your customer experience strategy to the next level.
Take a journey with leading brands demonstrating significant results in this large language model (LLM) era. While most Generative AI (GenAI) RAG options are getting caught up in legal and compliance issues, discover how some of our favorite brands are accomplishing customer self-service rates with modern virtual assistants.
Many experts are ignoring another option that delivers tremendous results. Explore how Fortune 500 consumer brands use LLMs for speed, ease, and scalability without risks. In this Tech Forum, we will deep-dive into real customer-facing results that compare and contrast to legacy virtual assistants that will soon become extinct.
Staples aims to help businesses of all sizes be more productive, connected, and inspired. With the introduction of generative AI (GenAI), Staples quickly recognized its potential to enhance the experience of store employees (Associates) by improving their ability to serve in-store customers and increasing their confidence, productivity, and job satisfaction. The company sought a partner to bring their vision for a conversational AI assistant capable of addressing both Associate and customer queries to life and found that partner in Quiq.
Since deploying its employee-facing GenAI Assistant, Scout, Staples has streamlined and accelerated access to information. Scout, an AI model trained on all things Staples, can instantly answer questions about policies, processes, products, and more, enabling Associates to assist customers and themselves efficiently.
Join this discussion with Natasha Bialecki, Staples CX Specialist, and Quiq Founder and CEO Mike Myer to learn:
- Key considerations when developing a GenAI Assistant
- Unexpected challenges encountered during the implementation of Staples’ first GenAI Assistant
- Strategies for scaling a GenAI Assistant rollout, including innovative approaches to drive Associate usage and engagement
Join us for an insightful roundtable discussion on the latest AI-powered tools revolutionizing the contact center landscape. We’ll explore cutting-edge technologies with a leading luxury retailer including agent assist, automated summarized notes, fraud detection, auto reships and automated email responses. This session is designed for CX leaders eager to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and security in customer interactions. Attendees will gain actionable insights into how these tools can streamline operations and elevate customer satisfaction.
Discover how AI can provide real-time support to agents, offering suggestions, answers, and guidance during customer interactions to improve response times and accuracy. Understand the role of AI in detecting and preventing fraudulent activities during customer interactions, safeguarding your business and customers and more!
In this discussion, you’ll gain practical tips on:
- Implementing agent assist tools to enhance real-time decision-making during customer calls
- Utilizing automated note summaries to improve agent productivity and reduce after-call work
- Integrating fraud detection systems to protect your contact center from security breaches
- Adopting auto reship capabilities to streamline the replacement process and reduce customer frustration
- Setting up automated email responses that maintain personalization while increasing efficiency
Astound Communications, an award winning internet service and 6th largest telecommunications company in the United States, faced common challenges in selecting and implementing an AI solution to enhance their contact center operations. Their objectives for AI were to increase productivity, lower attrition, reduce training costs, and enhance agent efficiency. Ultimately, Astound choose Agent X, deploying an LLM-driven QA solution.
In this discussion, HGS and Astounds Communications share a journey of understanding, evaluating, selecting, and implementing an AI-powered knowledge management solution. Learn how the implementation led to a comprehensive dashboard that boosted agent productivity, allowed for the leverage deeper insights, and offered a 360-degree of the customer to enhance the end user experience.
Gain key insights into:
- Criteria for Selection: Understand the specific criteria Astound Communications used to identify an AI solution that aligned with their goals.
- Cost Efficiency Gains: Find out in what ways an AI-based system can drive cost efficiencies.
- AI Implementation: Learn about what success looks and how to measure it when deploying of an AI-based intelligent knowledge management solution.
- Automated QA Solution: Explore how the integration of an LLM-driven automated QA solution further optimized operations.
- Agent X Solution: Discover why Astound Communications selected Agent X as their AI-powered contact center solution
When employees don’t feel valued or motivated to do meaningful work, the negative impacts are deep and wide. But where should leaders focus to make sustainable change? This workshop cuts to the core of employee apathy and arms leaders with actions that transform the perception of contact center work.
- Participants will explore:
- What are the root causes of employee apathy and how do you address the early indicators?
- Which methods are best for understanding employee sentiment, motivators, and detractors?
- How does clarifying and strengthening the connection between employee purpose and business goals improve performance?
In an era of rapid disruption in traditional car retail and financing, Chase Auto, a division of JPMorgan Chase, is leading the transformation of car buying and vehicle financing. Join keynote speaker Renée Horne, Chief Marketing & Customer Experience Officer, as she shares how Chase Auto is pioneering a shift towards innovative, customer-centric solutions that meet the evolving market demands.
Renée attributes her career success to being curious and a bit adventurous, in her keynote, she will discuss how passion for innovation allows Chase Auto to create a seamless, omni-channel car buying experience using advanced technologies and JPMorgan Chase’s extensive assets.
For manufacturers, Chase provides essential capital, financing, extensive marketing capabilities, customer data, an expansive branch network, and commerce solutions. For dealers, Chase Auto offers flexible credit options, alternative deal structures, and comprehensive banking services, transforming from a retail lender to a commercial banking partner. For consumers, Chase Auto revolutionizes the car buying journey with digital originations, pre-approved loan programs, and enhanced user experiences.
Renée will explain Chase Auto’s holistic approach to improving the automotive supply chain, providing reliable capital and services to manufacturers, financial solutions to dealers, and a seamless car-buying journey to consumers.
Join us to learn more about Chase Auto as they enable manufacturers to innovate, dealers to thrive, and consumers to achieve their vehicle ownership dreams, ultimately transforming the automotive industry.
Generative AI is the hottest topic in CX today, and one of its most promising applications is powering GenerativeAgent. A generative AI-powered virtual agent is as capable as Tier 1 agents to increase resolution and customer satisfaction. Your customers need a virtual agent that they can speak to naturally to accomplish tasks. Now they have one.
In this session, ASAPP and PTP will deep dive into this AI-led innovation and share how they partner with clients to deploy GenerativeAgent to deliver operational improvements, increased customer satisfaction, and reduced costs. You will witness firsthand just how powerful this technology is!
You’ll gain insights into:
- Ways GenerativeAgent unlocks business value and improve CX
- Real-world examples of how the ASAPP/PTP team is deploying GenerativeAgent with a Fortune 100 client and the results they are seeing
- Practical tips to get started on your organization’s GenerativeAgent journey, including best practices and process recommendations
The world is full of famous duos (Holmes & Watson, Batman & Robin, Han & Chewie), showing us that working together is better than going alone. The same can be said for the complex and ever-changing world of customer service. How can you be expected to stay up to date with the latest CX best practices when Generative AI is changing the game, sometimes by the hour? You need an experienced and innovative partner to navigate this ever-changing world and empower you to create craveable customer experiences.
By attending this session, you will learn:
- How Progressive identified the right partner to entrust with their customers
- How Progressive saves over $20M in annual operating expenses
- How Progressive achieves 97% intent accuracy to empower customers”
Mosaicx is a cloud-based solution that uses conversational AI, machine learning and natural language processing technologies to automate interactions with customers and employees. Its IVA technology delivers fast, easy, personalized service through industry-leading voice recognition and digital messaging capabilities, creating positive interactions that drive improved customer and employee satisfaction. Mosaicx makes conversational AI surprisingly simple.
AI in customer service is here. While some brands are still considering how it fits into their CX strategy, others are already hard at work implementing it in their day-to-day to handle volume, streamline processes, and grow customer loyalty.
In this panel led by Gladly, hear practical strategies and personal experiences from leaders on how they’ve applied AI across their support teams and found success.
They’ll discuss how to use AI to:
- Manage volume with intelligent solutions that meet every business need, from powerful self-service features to effective automation tools for agents.
- Scale and meet changing contact center needs, such as seasonal spikes in call volume, without increasing costs.
- Empower your agents to focus on high-value interactions — such as cross-selling and upselling — that drive revenue and customer satisfaction.
In an era where customer expectations continually evolve, transforming your organization to meet and exceed these demands is imperative. Join keynote speaker Kimberly Masters, Senior Group Director at Sam’s Club, as she unveils the journey of transformation that led to significant improvements in customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Kimberly emphasizes that a successful transformation starts and ends with an obsessive focus on enhancing experiences for members, customers, and associates. Achieving this requires a unified vision and measures of success across all levels, both internally and outsourced. Embracing boldness and the courage to challenge the status quo, coupled with integrating process, technology, and resources, is crucial. Timing is everything, especially concerning GenAI, and is essential for getting the experience right.
Her keynote will provide invaluable insights and actionable strategies for organizations looking to embark on their path to transformation, emphasizing the importance of a strong foundation, strategic alignment, and a bold, innovative vision.
Amanda Wiltshire-Craine, Senior Vice President and Head of Global Customer Services at PayPal, is a forward-thinking leader committed to personalizing customer experiences through technology and innovation. In her keynote address, she will discuss PayPal’s approach to customer service under the guidance of their new CEO and the brand’s ambitious three-year strategic plan to radically transform service delivery and operations.
With a focus on personalization and automation, PayPal is setting new standards for customer interactions. It is leveraging data and advanced technologies like AI and GenAI to become more predictive in how the organization surprises and delights its customers. Amanda will illuminate the journey toward completely reimagining servicing as more intuitive, empathetic, and universally accessible.
She is deeply passionate about diversity, equity, and inclusion as a leader, particularly in promoting leadership opportunities for women and people of color. Amanda aims to leave a legacy that empowers the next generation of leaders, making meaningful progress toward a more inclusive C-suite landscape.
Join Amanda to explore how PayPal’s innovative approach to service transformation can inspire your strategies for integrating technology with human-centric customer interactions.
Join us for an enlightening keynote with Emily Sarver, Vice President of Customer Experience at Lovevery, a subscription-based early learning company focused on child development. The brand, known for its dedication to social and environmental impact, has over 350,000 active subscribers and was named one of Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies in 2024.
Emily is an intentional, dynamic, and forward-thinking leader passionate about building and scaling world-class support teams. She leads from a place of conviction, characterized by a commitment to continuous improvement and a clear vision for the future. During her keynote, she will delve into the CX strategies that have fueled Lovevery’s growth and innovation, including using every interaction as an opportunity to build a meaningful relationship.
You’ll gain an understanding of how acting for the good of society and the planet and having purpose-driven leadership, along with a people-first culture, can help scale operations globally and advance a brand’s reputation while maintaining a solid customer-centric focus.
Attendees will walk away with actionable insights and be inspired to implement purpose-driven leadership within their own organizations to achieve operational success and make a meaningful impact.
Lead your contact center into a future where AI and human agents work together seamlessly. COPC will provide a comprehensive strategy that addresses the technical and emotional aspects of AI adoption.
Using the COPC AI Impact Change Planning tool, participants will gain practical strategies to analyze the impact of AI on agents and create a plan to navigate AI integration. Leaders will learn methodologies that ease the transition, improve agent satisfaction, and increase adoption.
Facilitators will begin by discussing how AI is changing the agent role, followed by an interactive session to methodically analyze the impact of AI in critical areas such as:
- Agent skills and knowledge requirements
- Recruitment and training
- Agent metrics and performance management
- Staffing requirements
- Agent perceptions of AI
This session will culminate in a discussion that brings this information to life to facilitate agent adoption. Leveraging the COPC AI Impact Change Planning tool, you will walk away with a strategy that transforms agent experiences with AI, making their jobs better and more fulfilling.
Unlock the power of employee engagement to drive exceptional customer experiences
in this interactive 1.5-hour workshop. This session explores the fundamental principles
of engagement and their practical application in the workplace.
Participants will:
- Dive deep into the core tenets of employee engagement
- Understand how the Great Place to Work (GPTW) survey aligns with
engagement principles - Analyze real-world examples of engagement initiatives tied to GPTW categories
- Develop actionable plans to address common engagement challenges
- Learn from OP360’s successful engagement strategies
Through group discussions, scenario-based problem-solving, and shared experiences,
attendees will gain insights into:
- Creating a positive work environment that enhances employee satisfaction
- Improving customer service outcomes through engaged employees
- Implementing effective communication, recognition, and growth opportunities
- Fostering fairness, purpose, and autonomy in the workplace
Leave with a toolkit of practical strategies to boost engagement, including:
- Flexible scheduling for work-life balance
- Recognition programs that motivate and inspire
- Professional development initiatives
- Wellness and inclusion programs
Join us to learn how to nurture a thriving workplace culture that benefits employees,
customers, and your bottom line.
Prioritizing enhanced consumer experiences is paramount for any consumer-facing brand. By integrating AI and automation, businesses can ensure timely and thoughtful responses to online consumers, freeing up resources to focus on efficiency, quality, and meaningful human interactions.
Join Kim McMiller, SVP Global Client Services at IntouchCX, and Luc Antoine, Head of Care at L’Oréal Canada, as they delve into how to harness automation for data integrity, aligning seamlessly with a global vision and deep understanding of consumer needs. This engaging workshop will highlight real examples from a top consumer brand and offer the unique opportunity to collaborate amongst your peers on leveraging automation, people, and processes to optimize operational efficiency and enhance the consumer journey.
The panel discussion delves into the intricacies of launching and sustaining AI-driven customer experience (CX) initiatives. The conversation will explore the landscape of AI implementation, emphasizing the elements necessary for successful deployment and continual support. Hear from Brands that have launched their AI strategies on what challenges they faced, the strategies they used, and the vital components they have planned to nurture and evolve their AI-based CX solutions beyond their inception. Get answers to real questions!
- What skills or roles are needed to stand AI up?
- What skills or roles are needed to sustain it?
- Where does AI for CX sit in the enterprise? Customer Service, IT, Product Management, or a brand new sub-team?
Join us for a workshop focused on how modern AI tools and Analytics are helping enterprises big and small establish the operational building blocks designed to breed a culture of trust and excellence. Learn about ways to distill and protect your data, while also being able to leverage that data across your operations to effectively coach and mentor your frontline, measure the effectiveness of your coaching process, and build a healthy and committed culture of continuous improvement at all levels.
AI is taking center stage when it comes to elevating customer service experiences. When we mix the smart capabilities of AI with the kind of empathy only humans can provide – that’s where the magic happens for both companies and their customers.
Our workshop will explore strategies combining the best technology with genuine, empathetic customer service to create experiences that truly differentiate and impact customer loyalty. Attendees will gain practical tips for prioritizing customer needs and emotions, ensuring seamless, personalized service that bridges the gap between digital efficiency and the human touch.
Sentiment… Language… Speech… QA… We all reference these terms, but do we know how to place tangible value on the human voice expressing such communication?
With the numerous human-based metrics used to manage corporate performance, most contact center operations have focused their investment decisions on advancements that remove the human component.
Yet, measures involving VoC, Promoters, and QA remain prevalent throughout all organizations. Many executives have sought to learn the true ROI involving sentiment… a high QA score… or even Top Box satisfaction. For many, attaching an ROI to these metrics appears daunting, moving them to a ‘necessary evil’ expense line. In the age of AI, we find ourselves pushing for investment success associated with corporate efficiency and reduced headcount, but how about the same rigor toward retaining humanity in our enterprises? Societal research continues to show that people resonate with and need personal connection. The relationship between our customers and brands should capitalize on that need while continuing to foster satisfaction with product offerings.
Hear from industry-leading executives who have capitalized on humanity’s power and created tangible business results. Then let’s collaborate as a Community to define what tangible success means for our Humanity Factors. Facilitated break-out tables will focus on customer sentiment, agent behavioral factors, customer satisfaction, and the difference between proactive and reactive communication analyses to design the next generation of ROI models as we embrace the AI era.
Dive deep into the future of financial services with Veronica Semler, Vice President of Servicing Operations at Oportun, as she demystifies the complex interplay between Generative AI and big data in revolutionizing the industry. Oportun, a distinguished FinTech provider committed to making financial goals achievable for over 2 million members, harnesses cutting-edge AI to reimagine customer service dynamics and operational efficiency.
This session promises a thorough dissection of AI-driven strategies reshaping how data is interpreted, consumed, and leveraged for decision-making. Witness firsthand how Oportun’s leaders, supervisors, and agents integrate these advancements to foster a culture of innovation, significantly enhancing customer experiences and driving financial success.
You’ll gain insights into:
- How consumable data eliminates the need for context switching and revolutionizes coaching and QA practices
- Real-world examples of how actionable insights derived from AI analytics empower staff at all levels to make informed, strategic decisions.
- The ethical considerations and governance of AI in managing sensitive financial data.
Join this live, power-packed session to see how AI-powered learning technology’s power has transformed the contact center training landscape forever. Training expert Casey Denby will deep dive into proven learning theory that has been incorporated into modern-day AI-based technology to scale learning efficiently and cost-effectively.
You don’t want to miss this session if you want confident, prepared, happy agents! Casey will share how leading brands such as United Healthcare, Bank of America, Verizon, Capital One, Prudential, Airbnb, Comcast, and many more have transformed their frontline training programs and found success via AI-Powered Simulation Training. Create the most lifelike, unbiased roleplay experience for your agents: it’s fast, flexible, and scalable.
In this session, you will:
Learn exactly what customers want from your brand and how you can best prepare your frontline agents to deliver through:
- Hands-on AI-Powered Simulation Training
- Understanding of ‘how people truly learn’
- Proven learning strategies you can take home and implement right away
- A live simulation build and practice that you can get your hands on and experience for yourself
Experience first-hand the potency of AI-Powered Simulation Training, as Casey shares:
- How to build a real-life simulation live
- Where GenAI is leveraged in the build
- A real simulated call scenario that you can practice live
Consumer expectations for customer service are higher than ever before – they expect to engage with businesses across multiple digital channels that are convenient, fast, and efficient. Join Amazon Web Services (AWS) to discover best practices for how to leverage phone, in-app and web calling, video, chat, short message service (SMS), and third-party messaging to deliver exceptional customer experiences.
In this session, you will learn about:
- Executing a true omnichannel strategy that delivers consistent customer experiences and better outcomes
- Empowering customers with self-service solutions for increased speed of service
- Driving high-velocity innovation in your contact center to improve your customer experience
Navigating Moments of Truth: A Human-Centric Approach to Employee Engagement and CX Excellence
Join Intradiem’s President and COO, Jennifer Lee, as she leads a panel of industry experts in a discussion that extends beyond the traditional focus to explore the heart of employee engagement, uncovering genuine “Moments of Truth” for both employees and the brand.
As technology continues to impact the type and complexity of live calls, employee experience must remain a focal point. CX leaders must reexamine the agent’s role and establish targeted, effective employee engagement support mechanisms to ensure agents are best equipped to deliver exceptional “Moments of Truth” in these new modern customer interactions.
The conversation will navigate the intersections between these pivotal moments, revealing how mutual support shapes a powerful synergy. Discover how these moments profoundly impact CX and explore strategies for combining technology and acknowledging the human touch to positively influence your “Moments of Truth.”
Key panel takeaways will include:
1. How to find and define your “Moments of Truth”
2. The mechanisms needed to modernize and streamline agent workflow
3. How to put training at the center of your employee experience and engagement
4. Taking a proactive approach with technology to enable a better EX
Are you wondering how to incorporate AI and Automation into your program effectively? Need help figuring out where to begin or how to create a compelling business case? Join Laivly along with Abercrombie & Fitch as they share insights on navigating the new landscape of AI technology in CX. Learn how to fund your tech projects based on cost savings and ROI from the first interaction.
Discover how to identify that crucial first step and develop a persuasive investment story. Learn from real-world experiences where an unexpected, high-value, compliance-based use case was the foundation for broader AI and Automation implementation.
In this discussion, you’ll gain practical tips on:
- Finding early ROI opportunities
- Crafting a smart expansion plan
- Future-proofing your AI strategy
Join us and embark on the path to AI and Automation success!
Today’s service delivery landscape largely focuses on technology-driven solutions thanks to emerging channels, cutting-edge tools, and AI-powered insights. But without a human-centric approach, you risk losing the emotional connection and empathy needed to unlock the value behind your investments.
Real transformation requires a human-centered design to succeed, so ensuring your service delivery approach is modeled around (and for) people is crucial to delivering outstanding customer experiences. In this session, Tadd McAnally, VP of CX Advisory services at VXI, will discuss prioritizing the human element by applying design-thinking principles backed by real-world examples and success stories in an increasingly complex ecosystem.
Join this compelling Customer Shop Talk to learn:
- How to assess your service delivery model and its maturity level
- How to ensure your transformation roadmap is collaborative, agile, and human-centric
- How to synchronize your entire service delivery network around your transformation efforts
Don’t miss out on this important session — or the opportunity to design with your people (not just bots) in mind.
Dive into the cutting-edge of AI and revolutionize your customer experience (CX). Whether you’re just starting or already on the path, this is your invitation to a game-changing dialogue on AI’s role in elevating both customer and agent interactions.
Discover the stark contrast between legacy architectures and the dynamic future promised by AI-infused technologies. Learn about AI’s power to seamlessly assist with post-call enhancement, provide next-best action recommendations, IVR and dialog flow customization, and enrich your knowledge base.
Join us to explore how wrapping AI around your current IT infrastructure can drive intelligence, foster innovation, and inject agility into your operations. This is more than a chance to upgrade your technology—it’s a pathway to reshaping your organizational landscape and redefining the CX you deliver.
A customer doesn’t think about channels. Some communicate only on one channel; some effortlessly flit across channels. But brands and their Customer Experience (CX) leaders don’t have that luxury. They must manage preferences across all their customers while trying to strike the balance of service excellence, operational costs, and an array of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities across channels.
How do brands manage the tension between serving customers however they want, in whatever channel they want, and proactively steering customers to channels to manage customer experience and efficiency?
This panel will dissect modern frameworks for crafting effective customer channel journeys. We’ll delve into customer behaviors across channels and the importance of fostering lifelong conversations that don’t just span channels but span over the entire customer relationship, moving beyond mere transactions. Insights from diverse brands will shed light on the evolving strategies and critical decisions in the era of customer experience AI and automation.
Join us as we explore the seamless channel experience. Our focus will be on how brands can balance operational efficiency and customer-centricity in the digital age, underscoring the need to delight customers, build meaningful connections, and drive lifelong customer loyalty in the constantly evolving customer service landscape.
In the fast-paced world of customer support, where quick responses and resolutions are crucial, the arrival of AI has been nothing short of revolutionary. Among the champions leading the charge in AI-driven customer support, AppFolio stands out. AppFolio is an Intercom customer that provides software applications and services for the real estate industry.
This session will dive into how innovative companies like AppFolio structure their customer service teams in an AI-first future. In particular, we’ll uncover how Appfolio was able to adopt this new technology and achieve substantive results quickly, including:
- Increasing their self-serve rate and automatically resolving 30% of customer inquiries using AI
- Decreasing overall response times and time to resolution
- Increasing trial conversions through proactive support
Strategic outsourcing can transform businesses by providing unmatched scalability and access to global talent and deep industry expertise. Despite its advantages, misconceptions like loss of control, quality decline, and remote team issues deter companies.
Driven by operational and financial constraints, Public Storage collaborated with OP360 to explore offshoring as a strategy for achieving customer experience and operational excellence.
This fireside chat will dive into the hurdles, challenges, and ultimately benefits that come with offshoring through the eyes of first-time outsourcer Public Storage. We will unbox their journey including:
- The driving force behind the outsourcing decision.
- The partner model and strategic approach.
- Achieved outcomes compared to initial expectations.
It’s often assumed that a decline in customer experience pays for gains in operational efficiency. That’s not the case for Bob’s Discount Furniture. They are leaders in both operational efficiency and NPS.
A customer-obsessed culture and great product value are the foundation of Bob’s brand. But more importantly, Bob’s also leverages digital channels and Generative AI at strategic points in their customer journey, allowing them to minimize phone contacts while still getting customers the information they need. It’s a win-win, offering great CX while minimizing costs.
Join a conversation with Quiq and Bob’s to learn:
• Insights into the techniques that Bob’s used to drive CX efficiency and the outcomes they achieved
• Understanding of the Generative AI Maturation Curve that Bob’s is using to plan the adoption of safe Generative AI
• Suggestions about how to navigate organizational challenges, risks, and barriers to AI “
Even the most reputable companies strive for constant improvement in today’s fiercely competitive business landscape. As technology reshapes traditional operations, it has become imperative for organizations to foster consistency, increase efficiencies, and create a high-performance culture. Join us for an insightful session featuring Lance Gruner, Mastercard’s Executive Vice President of Global Customer Care, and Kyle Kennedy, President and CEO of COPC Inc. They will reveal how Mastercard’s commitment to excellence led them to adopt and implement a unified performance management framework. Lance will share Mastercard’s impressive journey and its sustained impact on the organization and its customers. Don’t miss out on the chance to hear Mastercard’s story of continued success in the face of rapid change, solidifying its leadership position in the CX industry.
In today’s tech landscape, the promise of conversational automation has captivated industries, offering unparalleled opportunities for customer interaction. Join Knowbl as we delve into the transformative potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) and their role in fulfilling this long-awaited promise.
This Tech Forum session aims to dissect the fundamental distinctions between RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) LLMs and shed light on the nuances that differentiate these technologies in conversational AI.
Moreover, we’ll be navigating the critical compliance landscape within conversational automation. While guardrails are essential, the Knowbl team will illustrate why a compliance-approved approach necessitates more than mere guidelines, showcasing how Knowbl tackles this challenge effectively.
Amidst the conversational AI buzz, this Tech Forum seeks to transcend the hype.
Attendees will:
- Learn why leading brands are embracing this technology’s solutions.
- Uncover tangible applications, success stories, and real-world scenarios where these solutions have reshaped customer experiences for enterprises.
- Understand the differences between RAG and LLMs.
- Grasp the potential of LLMs in transforming how customers interact with brands, marking a significant shift in the dynamics of customer-brand relationships.
In the dynamic world of technology, conversational automation has emerged as a groundbreaking tool, captivating industries with its potential to create measurable positive outcomes in customer engagement. This Tech Forum session offers a unique opportunity to delve into the success story of Home Depot, a trailblazer in redefining customer experience through the adept use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in a manner that is both safe and compliant.
We will explore the intricate distinctions between Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and LLMs, drawing valuable lessons from Home Depot’s journey. Their approach exemplifies how conversational automation demands more than just guidelines and guardrails; it requires a strategic, transformative mindset crucial for achieving success in this domain.
Key takeaways will include:
- Confidence in Automation: Understand how embracing conversational automation in customer service can lead to significant benefits, offering a high return on investment. This segment will showcase concrete examples from Home Depot’s journey, highlighting key outcomes around containment and call resolution rates.
- Practical Roadmap: Gain insights into initiating and navigating the journey of conversational automation. We will dissect the essential considerations and steps necessary to implement this technology effectively, drawing from real-world experiences and the successes and challenges encountered by Home Depot.
- Understanding the Urgency to gain better Outcomes: Grasp the potential repercussions of delaying the adoption of conversational automation. The session will emphasize the urgency of integrating this technology to stay competitive and relevant in the rapidly evolving tech landscape.
- AI Fundamentals: Learn key differences between Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and LLMs and why they matter to you as a leader.
This enlightening keynote address will dive into the transformative impact of customer-centric strategies on business success. In this engaging talk, Tracy Sedlak, VP of Customer Success at Offerpad, unravels the pivotal role of harnessing Voice of the Customer data in shaping robust business strategies, fostering a culture of customer-centric excellence, and embracing the power of stepping outside our comfort zones to glean unparalleled insights from customers.
Discover how these invaluable insights are not just indicators but catalysts for innovation and growth, driving organizations toward a future where understanding and leveraging the customer’s voice are at the heart of every strategic decision.
You can hear more about Tracy’s brand story and leadership journey at CRS Tucson.
Every business speaks to customer satisfaction and values what a CSAT measure can tell them, but the most significant contributor to customer loyalty sits inside of your own organization. Your corporate culture dictates your customers’ satisfaction. What happens inside of your own four walls is as important as what occurs outside of them. Hear from the President and CEO of one of the nation’s most respected brands on how he fosters culture to drive satisfaction.
Philip Walker is the President and CEO of AAA Life Insurance Company, the life insurance business supporting the vast AAA membership – one of our nation’s most recognized membership organizations with over 60 million members.
Philip is a senior executive with 30 years of experience building and growing strong financial services companies. He will share how he delivers value to AAA’s membership base by understanding their needs and inspiring his team to develop a service-mindset. His vision to foster this corporate culture to serve the AAA member has grown the life insurance business and created loyalty within the overall AAA membership.
When you love the great outdoors, it makes sense to try and do everything you can to protect it. That’s why Arc’teryx, the high performance outdoor equipment brand, is doing its part to consider its environmental impact every step of the way. The brand is committed to incorporating sustainability and circularity into every business decision, making them integral to its core business.
Join Dave Pitsch, Vice President of Guest Services at Arc’teryx, as he addresses the brand’s unwavering commitment to delivering a premium guest experience and investing in its guests throughout the entire lifecycle of its products. The brand’s emphasis on performance, attention to detail, and dedication to environmental responsibility has garnered a strong reputation among outdoor enthusiasts.
Learn how the brand is shaping the future of guest experience, addressing crucial moments of truth, and aligning its product design, circularity initiatives, and guest services to cater to the evolving needs and expectations of its guests.
This enlightening keynote address will dive into the transformative impact of customer-centric strategies on business success. In this engaging talk, Tracy Sedlak, VP of Customer Success at Offerpad, unravels the pivotal role of harnessing Voice of the Customer data in shaping robust business strategies, fostering a culture of customer-centric excellence, and embracing the power of stepping outside our comfort zones to glean unparalleled insights from customers.
Discover how these invaluable insights are not just indicators but catalysts for innovation and growth, driving organizations toward a future where understanding and leveraging the customer’s voice are at the heart of every strategic decision.
You can hear more about Tracy’s brand story and leadership journey at CRS Tucson.
Simplifying Contact Center Processes to Drive Cost Savings and Better Experiences
The contact center industry plays a pivotal role in delivering efficient customer service and support across various sectors. However, operating a contact center can be costly, primarily due to the highly labor-intensive nature of its operations. To address this challenge, organizations are increasingly turning to automated process flows to optimize their contact center operations and achieve significant cost savings.
Join us as we share the remarkable transformation journey for PSCU, the nation’s largest credit union service organization, and how they leveraged AI and automation to simplify hundreds of workflow processes and eliminate their complicated knowledge base—all while boosting agent performance and efficiency.
By streamlining and automating data retrieval and consolidation, knowledge management, and issue escalation processes, agents can dedicate their expertise to more complex, value-added tasks. This not only amplifies their productivity but also elevates customer satisfaction by ensuring faster and more precise resolutions.
In this session, Kim West, VP Product Marketing from Uniphore, will share invaluable lessons and key takeaways to:
- Harness the power of AI to automate knowledge search and time-consuming tasks
- Ensure compliance with industry regulations through guided workflows
- Drive retention by empowering agents to focus on the customer experience
SmileDirectClub Facility Tour
Join Execs In The Know on Friday, September 22nd at 2 PM for an exclusive behind-the-scenes tour of SmileDirectClub’s manufacturing facility, dubbed the SmileHouse.
Your host Alvin Stokes, SmileDirectClub’s Chief Customer Contact Officer, will share how this disruptive brand streamlines the process from customer engagement to purchase decision and innovates the CX journey for their customers. He’ll delve into the fascinating connection points between customer experience and the SmileMaker Platform, which uses advanced AI technology via an app to put game-changing innovation in the palm of consumers’ hands.
Be a part of this tour to witness firsthand the impressive 3D printing technology, observe the seamless production of the brand’s clear aligners, and explore how using the power of innovation can up-level your customer experience. We can’t wait to see you there!
Unleashing the Power of Customer Data: How iRobot Leverages Customer Care to Build Lasting Relationships in a Competitive Tech Landscape
As a leading robotic vacuum cleaning company, iRobot prides itself on being a mission-driven builder that is revolutionizing the way the world cleans with consumer robots. In this thought-provoking keynote, Ledia Dilo, VP – Head of Global Customer Care and Fulfillment at iRobot, will address how the brand leverages customer-centric strategies to drive sustained growth, optimize operations, and build customer loyalty in an industry currently challenged by slowing demand, growing competition, and supply chain cost.
With a focus on optimizing operations, she’ll unveil the four strategic pillars that drive iRobot’s customer interactions, streamline onboarding experiences, and transform the contact center into an insights-driven and strategic business unit. Additionally, she’ll highlight the crucial role of the care team, their technical training, and collaborative partnerships with engineering in addressing complex product issues. Find out how iRobot leverages customer data and proactively engages with consumers to build lasting relationships. Drawing on her extensive experience, inspiring anecdotes, and metrics showcasing the success of proactive initiatives, she will demonstrate the immense value of customer-centricity in shaping the trajectory of brands to deliver win-win outcomes.
Join Ledia to gain insights on iRobot’s remarkable legacy that will inspire you to reshape your brand’s customer experience, unlock new growth opportunities, and cultivate enduring customer loyalty.
Size Is No Barrier: How Brands of Every Scale Are Navigating the AI-CX Landscape
Join our panel of experts as they delve into the world of artificial intelligence (AI) and its potential transformative impact on customer experience (CX). The revolutionary capabilities that AI offers enable brands to drive meaningful change by delivering efficiency, hyper-personalization, predictive insights, and seamless interactions to just name a few.
This thought-provoking discussion will shed light on a wide range of perspectives, various use cases, and challenges and opportunities that are specific to an organization’s size and structure when deploying AI in the current CX landscape. Our panelists will also share how they are navigating critical considerations, such as ethics, data privacy, and striking the right balance between automation and maintaining a human touch.
LOOP Insurance Replaced Their Chatbot with Generative AI and Resolution Rates Soared!
The latest AI has the potential to automate far more customer inquiries than prior generations of conversational AI. While most people are familiar with ChatGPT, few have deployed Large Language Models in customer-facing applications.
LOOP Insurance is excited to share their journey from a simple chatbot to a state of the art LLM-powered AI assistant that has yielded an impressive increase in effectiveness and CSAT.
In this session you will learn:
- How LOOP’s new AI Assistant is remarkably better than its prior generation chatbot
- What resolution rates and outcomes LOOP achieved
- How LOOP was able to harness the power of LLMs to serve customers safely
From Ordinary to Extraordinary Customer Support: A Real-World AI Success Story
Witness the transformative journey of iPostal1, the worldwide leader in digital mailbox technology, as we explore the extraordinary impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on customer service. Due to rapid growth and an influx of customers, the brand was challenged to rethink how it could maintain its high standards for an exceptional level of service.
Armed with innovative solutions and a dynamic suite of tools, iPostal1, was able to scale its operations and take control of how it managed relationships with customers without diminishing the quality of its customer service.
Join us to hear from Dan Medina, Director of Customer Service Operations at iPostal1, and Colin Crowley, CX Advisor at Freshworks, to learn how AI can empower your customers, agents, and leaders alike by:
- Deflecting queries and automating repetitive tasks
- Building efficiencies to enable improved customer resolution times and retention
- Saving agents time and getting to contacts in under a minute
- Equipping teams with valuable insights to improve operational efficiency and focus on what matters most
Achieving Cultural Alignment: Neiman Marcus Sets the Stage for Optimal Strategic Partnerships
The cultural alignment between your organization and your BPO partner has become an essential ingredient to drive performance, speed to proficiency, and a consistent customer experience across locations. When cultural alignment is measured, monitored, and continuously calibrated, both companies arrive at a greater understanding of each other’s beliefs, communication processes, and abilities—functioning with truly dynamic collaboration.
In this session, learn how Qualfon and Neiman Marcus’ cultural alignment has resulted in the ultimate strategic partnership.
- Measure your company culture using internal NPS and surveys
- Integrate your company culture into your BPOs training curriculum to produce brand ambassadors
- Discover the results that are revealed with a culturally aligned partnership
The Future of Work: Navigating the Change Curve
In a rapidly changing world, the landscape of work and business is undergoing unprecedented transformations. During his keynote, Peter Mallot, Worldwide Support Leader for Modern Life and Business Programs at Microsoft, will provide an informed perspective and timely insights at the intersection of Workforce Strategy, Culture, and Technology.
The future of work is progression, not an overnight solution. It demands a shift in corporate culture, management philosophy, and workforce adaptation, where the focus moves from reactive to proactive, from support to achievement. The path forward lies in a delicate balance between leveraging technology’s capabilities and empowering people toward greater productivity, collaboration, flexibility, and automation to enable customers to achieve more.
Join Peter to gain a deeper understanding of the engine required to drive change for an organization’s most valuable assets — its teams and its customers.
Behind the Screens: How MoviePass Is Redefining Customer Experience and Building a Moviegoer Community
In this engaging keynote address, Stacy Spikes, CEO of the nationwide movie subscription service MoviePass, will take you on a journey where customer-centricity and innovation converge to create immersive and personalized cinematic experiences for all.
Discover how MoviePass is reinventing itself post-bankruptcy, overcoming past challenges, embracing product and customer service improvements, and setting its sights on a new horizon. From navigating customer churn to building customer trust and loyalty, Stacy will share real-life examples of the pivotal moments and invaluable insights that are shaping the brand’s trajectory.
Learn why diversity and building community are not just cultural values, but smart business moves that lead to better products and greater market reach. Additionally, Stacy will delve into the potential of blockchain technology as a powerful tool to bridge the gap between moviegoers and filmmakers.
Join us for this thought-provoking and inspiring look into the future of cinema and Stacy’s ambitious plans for reinventing moviegoing for customers.
Finding the ROI of Your CX Vision
As CX leaders, we recognize that enabling a customer-centric vision holds immense potential for driving value for our organizations.
Join our esteemed panel of industry experts as we explore how CX is used to drive revenue opportunities and strong business value. The panel will unlock the key KPIs and performance metrics that leaders must be measuring and monitoring to validate and amplify the value of their CX vision. With an ever-changing technology landscape alongside evolving customer expectations, we will explore the future impacts of CX ROI and discuss the influence it will have on what we measure.
From this session you will take away:
- The CX outcomes that can drive value to your organization.
- Effective KPIs and performance metrics that demonstrate the value of your CX initiatives.
- Considerations on how to measure and evaluate your future state of CX.
Creating a Healthy, Tech-Empowered Workplace
Technology is most effective when it’s used in the service of human beings. Join Intradiem President Jennifer Lee for a customer case study featuring Jim Simmons from Synchrony Financial. Jennifer will discuss technology-driven strategies to boost employee well-being and performance, and Jim will explain how Synchrony Bank is leveraging automation along with Thrive’s science-backed behavior change platform to provide more human-centric support to its contact center agents. Arianna Huffington, founder and CEO of Thrive Global, will share via video how Thrive embeds employee well-being into everyday workflows, which lowers stress, builds resilience and improves performance.
The Lifelong Conversation: How to Make Customer Service Your Business Using a Seamless Channel Experience
In today’s competitive business landscape, customer service has become the ultimate differentiator. It’s no longer just about resolving issues; it’s about creating meaningful connections that foster loyalty and advocacy. Channel shouldn’t matter when it comes to delighting customers. The modern customer service team needs to meet customers where they are without having their information siloed across tools or channels. This panel discussion will bring together industry experts, thought leaders and seasoned practitioners to explore effective strategies and best practices for cultivating lifelong conversations with customers. Through engaging dialogue and insightful anecdotes, the panelists will highlight the key elements contributing to making customer service the centerpiece of your business by establishing a seamless channel experience that transcends traditional boundaries.
The Era of Intelligent CX: Opportunities and Challenges
We all see it coming, an AI revolution that is more than just hype. However, figuring out how to make it work smoothly for customer service and finding the best way to learn, evaluate, and put it into action is not a walk in the park.
Join us as we examine the opportunities for leveraging AI to better understand, shape, customize, and optimize the customer journey and your overall CX. We’ll share real-world success cases and even a few cautionary tales of when things didn’t go quite as planned.
During this Shop Talk, you’ll leave understanding:
- The unique requirements and considerations for applying AI in a CX setting.
- Ways to identify opportunities for AI to bring real value to your CX organization, in hours and not years.
- The future role of an agent, and how their interaction with the customer will change in the short, medium, and long term.
What Is a Digital Worker?: Harnessing ChatGPT and Automation to Create New Strategies in CX
Enter digital workers, where AI and automation meet to support employee and customer experiences. They are changing our understanding of the future of work.
To support human employees, digital worker technology will continue to advance capabilities. The unique capabilities of Generative AI and automation are enabling CX leaders to gain a deep understanding of customer preferences, behaviors, and pain points.
Join us as we explore a real-world example of how a leading brand harnessed digital workers to revolutionize its contact center operations.
During this Shop Talk, you’ll discover:
- How digital workers can connect with customers by performing tasks guided by the power of Generative AI technology to provide consistent, on-brand CX.
- Ways to layer this technology onto your existing systems to overcome traditional tech blockers and modernize your customer care strategies.
- The tangible outcomes achieved by real-world clients, including accelerated productivity, exceptional first-contact resolution, and elevated customer satisfaction.
- How to leverage this technology in new ways to enhance agents and scale up customer service
Digital First, Member Always: How Navy Federal Credit Union Brings this Mantra to Life
Navy Federal Credit Union (NFCU) has always been focused on providing member-first service to more than 12 million global customers, and their frequent recognition by Forrester, KPMG, and JD Power reflects that emphasis. With the advent of more advanced technology, NFCU has worked hard to strike a balance between the high-touch interactions and digital journeys they provide to members. To guide this work, NFCU adopted a Digital First, Member Always philosophy.
In this session, we will share a glimpse into some of the ways the NFCU customer experience teams are bringing this mantra to life. Starting with the fundamentals, we will discuss key initiatives that are improving the member’s digital journey.
You will learn about:
- How NFCU got started on this journey and how the philosophy drives the organization’s focus
- Some of the new capabilities and processes NFCU has launched to achieve this balance and recent results that highlight success
- Future plans for additional digital self-service capabilities, including expansion of multi-channel bots and large language models (e.g., ChatGPT)
We hope you will join us to hear about NFCU’s exciting journey as they deliver compassionate service that strives to always put the member first!
Data-Driven Customer Insights: Leveraging Analytics to Anticipate and Exceed Customer Expectations
As artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technology evolve, contact centers are using them to transform customer experiences through agent assist, self-service, and conversational analytics capabilities.
Join Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Truist to discover best practices for how to leverage AI-powered technology to deliver exceptional customer experiences. In this session, you will learn about:
- Executing a connected channel strategy that delivers consistent customer experiences
- Leveraging AI/ML for real world outcomes like better self-service, agent assistance, and conversational analytics
- Turning data into insights that drive continuous improvement of your customer experience
The Agent, the Data, and Technology: Three Pillars for Enabling CX Personalization
With the global CX personalization market forecast to hit $11.6 billion by 2026, it is imperative that brands embed true personalization opportunities across the service journey. Facilitation begins with bi-directional omnichannel engagement that will require cutting-edge technology, insightful analytics, and advanced agent enablement.
This incredible panel will showcase agents alongside their business leaders in what is sure to be a powerful conversation on the approach needed to radically transform customer relationships. Join us as we unpack and explore critical insights from two unique perspectives on:
- What agents need to enable next-level personalization
- The influential role of agent empowerment in reaching CX goals
- How advanced analytics will unlock new opportunities
- Reaching the goal of moving Customer Service from a cost center to a profit center
- The role of technology and how it sets frontline agents up to create even more meaningful relationships with customers
Ignite the Leader Within: Embracing the Power of Inspiration for Extraordinary Results
Inspiration is a catalyst for greatness. It transcends the mundane and ordinary, breaking through conventional boundaries to unleash the full potential of individuals and teams. In this captivating keynote, Carolyne M. Truelove, Vice President, Reservations and Customer Relations at American Airlines, will unveil the immense power of inspiration and its ability to ignite a drive for exceptional results and lead transformative change.
Discover the extraordinary possibilities that lie within you as a leader. Everything a leader does requires connection, including vision, strategy, and execution. Learn the art of connected leadership, fostering a culture of open-mindedness, and leveraging your leadership to navigate through the ever-evolving business landscape. When inspiration permeates every aspect of an organization, magic happens. Join Carolyne for an unforgettable keynote and unlock the secret to inspiring others into action.
Leading Across Generations: Understanding and Embracing Differences in the Modern Workforce
As the workforce grows and diversifies, leading across generations has become more challenging than ever before. There are now five generations in the workforce (Silent Generation, Baby Boomers, Generation-X, Millennials, Generation-Z), each with unique values, communication styles, work preferences, motivators, and technology habits. This can lead to misunderstandings and incorrect assumptions among colleagues, making it critical to welcome different perspectives and use them to lead effectively.
In this workshop, COPC Inc. will present 2023 research that illuminates the reality of generational divides in contact centers and customer experience operations.
Attendees will:
- Learn the characteristics, preferences, and drivers of each generation and their impact in the workplace
- Discuss how to gather similar insights and data from their employees
- Uncover effective leadership methods for each generation, while understanding the importance of individual management styles for each person
- Create a leadership enhancement plan based on shared research and best practices (participants can bring their own data if they have it)
- Share thoughts on how to ensure generational awareness is spread throughout the management chain down to frontline management
Join COPC and your peers to learn how to transform your leadership approach and create a culture that welcomes generational differences. Leave this session with a better understanding of how to lead and manage each generation while maintaining individual strategies for maximum success.
Building Trust in Generative AI
Generative AI brings forth a new realm of possibilities for enhancing the customer experience. However, its propensity to occasionally deliver inaccurate or nonsensical information — a phenomenon known as a hallucination — could potentially impact hard-won customer loyalty. To ensure its success, generative AI has to solve problems and respond in a way that is accurate, helpful and free from toxicity and bias.
Join AI experts from TELUS International, a leading digital customer experience provider, for a Tech Forum exploring:
- The emerging technologies and processes that are being deployed to increase the accuracy of generative AI models.
- Potential legislation, similar to the AI Bill of Rights, being proposed in the wake of the generative AI explosion.
- Consumer perception of AI-generated content, including accuracy, completeness, attribution and age-appropriateness.
- And more!
How to Cultivate a Culture of Well-Being for a Resilient Workforce
Companies today require a robust well-being strategy to have a material impact on the growing crisis of workplace mental health and business resilience. Join us for this interactive session as we explore the Four Building Blocks of Emotional Intelligence. We’ll be exploring how to intentionally cultivate learning, development, and leadership strategies that focus on mindfulness and emotional intelligence, and how they are enhanced by dynamic neuroinsights and AI technology.
Key takeaways:
- Learn how well-being helps to drive retention, effectiveness, and efficiency gains throughout the workforce.
- How well-being technology programs leverage AI to assist with the timely delivery of well-being interventions.
- Ways to deeply integrate holistic system design and well-being practices across the employee lifespan.
The Conversational AI Divide
There is a great divide emerging in customer experience (CX) and leaders are being presented with the opportunity to blaze a trail forward with Conversational AI to set themselves apart in their service experience.
Conversational AI presents the opportunity for companies to harness new technology in a low-risk, high-impact environment. Embracing these new possibilities makes it possible for CX leaders to deliver enhanced and effective service at scale.
During this Tech Forum, you will be guided through the steps and considerations needed to build your very own AI assistant. Participants will walk away appreciating how simple and risk-free it can be to deliver big CX wins.
Join us as we explore:
- The universal presence of AI assistants: Understanding how AI assistants are becoming ubiquitous, shaping the future of customer interactions across industries.
- Building better customer experiences with reduced levels of effort: Discovering strategies to leverage Conversational AI to streamline and enhance the customer journey, delivering seamless experiences that require minimal effort from customers.
- The ease of creating your very own virtual AI assistant: Exploring the possibilities of building custom AI assistants without the need for extensive coding or AI expertise, opening new avenues for innovation and personalized experiences.
- Uncovering the distinct advantages and untapped potential that can be leveraged by embracing Conversational AI and staying at the forefront of this evolving landscape.
Don’t miss this opportunity to bridge the Conversational AI divide and unlock the full potential of AI assistants in revolutionizing your CX.
Improving EX in a Remote Workforce
In today’s remote work environment, organizations must not only hire the right talent but must also leverage technology to effectively manage and improve the employee experience (EX) throughout the agent life cycle.
To boost agent experience and reduce cognitive load, leading organizations are:
- Using job simulation previews to set realistic expectations
- Helping accelerate onboarding and training through micro-module learning and personalized AI avatars
- Managing agent stress and anxiety with rapid employee feedback and real-time reporting
- Applying generative AI across EX to drive improved satisfaction
In this 90-minute session, we’ll explore how to best empower remote employees and motivate them to foster collaboration amongst themselves as well as with managers. With effective strategies in place, companies will see higher ESAT, engagement, and retention from happy and productive team members.
AI Simulation Roleplay Training for Speed to Proficiency in the New Hybrid Workforce
As you build onboarding for new hires, getting your agents to a place of confidence and proficiency can often be a challenge, especially in a hybrid workforce environment.
In this interactive session, we will reveal key findings on CX preferences designed for today’s consumers and what experiences they truly expect when contacting your brand for support. Find out why driving higher speed to proficiency with new hires is the top metric for delivering the experience your customers expect and deserve.
The hybrid workforce is here to stay. Learn insights into why companies are losing customers and market share by not having effective onboarding. While companies shifted to ‘virtual learning’ due to need, most lack a cohesive and scalable training and onboarding strategy for new hires in a global hybrid workforce.
In this session you’ll learn:
- The most effective methods to onboard new hires in a global hybrid workforce
- Best practices from your peers that are leading the charge in driving speed to proficiency
- Key findings on CX preferences impacting your business
- How to best scale onboarding consistency and accountability
- Which innovative technologies can be leveraged to achieve key outcomes
JACK MEEK
Vice President, US Care Support Operations, GoDaddy
Jack Meek currently leads customer care operations at GoDaddy, the world’s largest services platform for entrepreneurs around the globe. GoDaddy’s mission is to empower their worldwide community of 20+ million customers — and entrepreneurs everywhere — by giving them all the help and tools they need to grow online. With 21M+ customers worldwide and 84M+ domain names under management, GoDaddy is the place folks come to name their idea, create a compelling brand and a great looking website, attract customers with digital and social marketing, and manage their work. Jack is responsible for developing and executing the future global care strategy that will continue to differentiate GoDaddy as the advocate of small business success throughout the world.
Jack is an influential change leader who has a passion for technology, innovation, and seeing people succeed. His foundational expertise and passion for building a solid employee and customer centric culture started at MCI where he was repeatedly recognized for record-breaking performance & leadership achievements. He then went on to help build and consolidate large-scale customer service and sales organizations at in the Telecom and Retail Energy space. Jack has successfully transformed and maintained customer operations and sales organizations of all sizes and across many different industries. He spent several years as a senior leader in the Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) industry helping multiple clients such as Verizon, Sony, and T-Mobile achieve their customer outcome goals.
JEFF MYERS
Vice President and General Manager Customer Care, SiriusXM
Jeff is a passionate advocate for Customers and designing frictionless experiences for them. He began his career in Marketing in 1991, as a call center agent, while attending the University of Wisconsin, Madison and studying Communication Theory and Research. The first eight years of his career included multiple call center operational roles. Following his first eight years in operations, Jeff spent 10 years in the Omnicom family in both the US and the UK/Europe with multi-channel responsibility for Client Services and Program Strategy in a variety of verticals including Telecom, Energy, Media and Non-Profit. He currently serves as the VP and GM of Listener Care for SiriusXM with responsibility for all live customer interactions. His scope includes partnerships with 16 BPOs, in nine geographies, representing more than 60 support center locations.
Bill Colton
Co-Founder and CEO, Global Telesourcing
Bill Colton is the Co-Founder and CEO of Global Telesourcing, a premium provider of digital and voice customer experience and sales solutions for some of the largest and most recognizable brands in the US. Using native-speaking English agents who spent their formative years living in the US, their workforce is as bi-cultural as they are bi-lingual. Global Telesourcing serves clients from centers in both Monterrey and Leon, Mexico, as well as work-from-home.
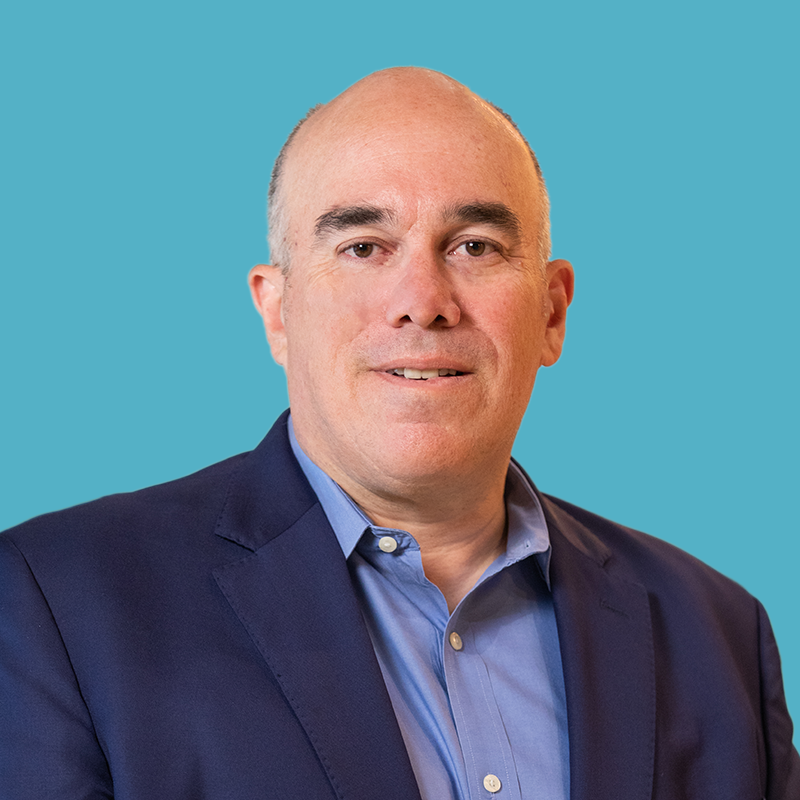
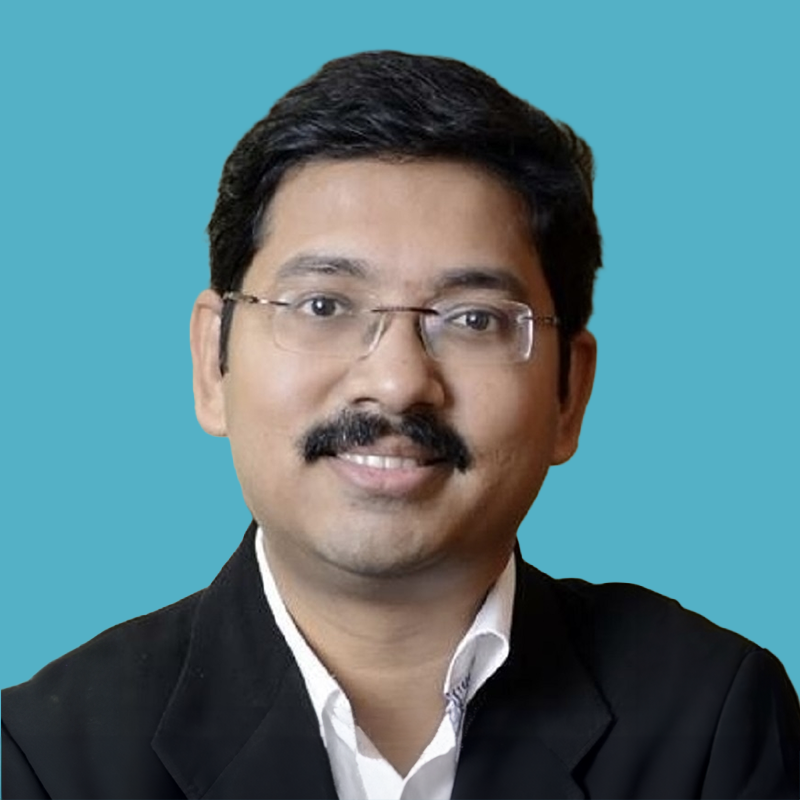


















































































































 TELUS Digital
TELUS Digital




















 Trista Miller
Trista Miller



























